2
Primary Care and Other Health Care Professionals
Dorothy Howell, DHA, MSN
Whitney Hamilton, DrPH
Melissa Jordan, DHA, EdD
Middle Georgia State University
“The moral test of government is how that government treats those who are in the dawn of life, the children; those who are in the twilight of life, the elderly; and those who are in the shadows of life, the sick, the needy, and the handicapped.” – Hubert H. Humphrey, 38th Vice President.
Learning Objectives
- To explain the basic principles of Primary Care
- To discuss the role of key primary care practitioners
- To describe the various types of Nursing Care Practitioners
- To examine the various roles of drug therapy professionals
- To review the roles of specialty care professionals
Introduction
The American Academy of Family Practitioners (AAFP), (2021) describes primary care as care provided to the patient, the system delivering care, and the clinicians providing primary care. In primary care, physicians and their healthcare teams provide integrated, readily accessible, patient-centered, low-cost services that will yield high-quality health care outcomes.
Primary care encompasses health promotion, disease prevention, health maintenance, counseling, patient education, and diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic illnesses that are delivered in many types of health care settings such as hospitals, nursing care facilities, managed care organizations, outpatient facilities, laboratories, etc.
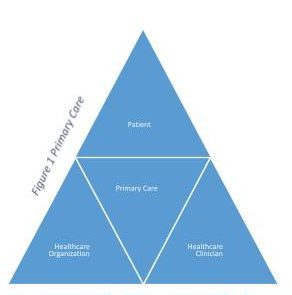
Furthermore, primary care can be described based on the following categories in Figure 2:
Figure 2
Categories of Primary Care
The American health care system is vast, complex and powerful. It is run by various types of for-profit and non-profit entities, indicating the need for a well-educated and diverse labor force of healthcare professionals. Most practicing healthcare professionals are licensed by professional licensing boards that seek to protect the health and safety of the public from fraudulent and unethical practitioners. This chapter provides an overview of primary care and other health care professionals. The discussion will include the role of the health care professional, required training, and practice settings in which they are employed.
Overview of Primary Care Practitioners
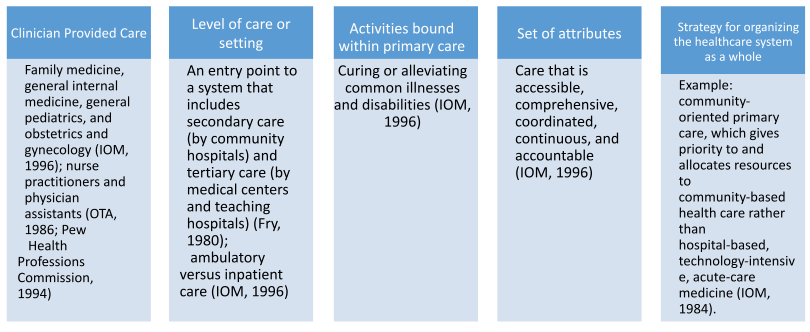
Understanding the role of a primary care practitioner requires knowledge of primary care in general. The Institute of Medicine in 1994 provides the following description of primary care: “Primary care is the provision of integrated, accessible health care services by clinicians who are accountable for addressing a large majority of personal health care needs, developing a sustained partnership with patients, and practicing in the context of family and community”. Primary Care is the patient’s point of entry or initial contact with the health care system (Shi & Singh, 2015). It is patient-centered and views the patient as a holistic being. The purpose of primary care is to coordinate the provision of health care services between the patient and the components of the health care system. Primary care providers evaluate, diagnose, treat, refer, consult, monitor, follow-up, advise, and advocate for the patient in efforts to provide continuity of care. Primary care also focuses on disease prevention (Shi & Singh, 2015).
Generalist/Medical Doctor/Physician
The terms generalist and medical doctor are used interchangeably to describe a graduate from a school of medicine who is a board certified, licensed practitioner providing a broad spectrum of care within his/her own specialty (IOM, 1996; Miller-Keane Encyclopedia and Dictionary of Medicine, Nursing, and Allied Health, 2003). The Farlex Partner Medical Dictionary (2012) defines a generalist as an internist, family physician, or pediatrician who performs general medicine in the treatment of nonsurgical diseases. A family physician is a medical specialist who plans and provides the comprehensive, continuous primary health care of all members of a family, regardless of age or sex. The attending physician visits the patient in hospital settings to provide direction for treatment. An emergency physician works in the emergency room to provide emergency care to the injured and individuals presenting with various types of healthcare conditions such as a heart attack, stroke, allergic reaction or influenza. A resident physician is a graduate from a school of medicine and a licensed physician learning a specialty through in-hospital training (Miller-Keane Encyclopedia and Dictionary of Medicine, Nursing, and Allied Health, 2003).
Generally, an individual pursuing a medical degree must have a 4-year baccalaureate degree, premed science coursework, and pass the Medical College Admission Test (MCAT). Individual medical schools may require different qualifying scores for admission. Medical schools issuing the Doctor of Medicine (MD) degree or the Doctor of Osteopathic Medicine (D.O.) degree are accredited by the Liaison Committee on Medical Education (LCME), which is a 4-year degree program of course work and clinical rotations. A D.O. is trained in osteopathic or manipulative medicine, which is a form of manual therapy focusing on improving ailments of the musculoskeletal system. Their focus is preventive care and holistic patient care (GKEN, 2009). A MD is trained in allopathic medicine focusing on using active interventions in disease treatment so that the effects of the disease will be minimized (Shi & Singh, 2015). Medical school graduates complete a 3-7 year residency program in a teaching hospital. An additional 1- 3 years of training is required for doctors desiring to specialize in a subspecialty field of practice. Once residency is complete, the doctor must pass all three phases of the United States Medical Licensing Examination (USMLE) or the Comprehensive Osteopathic Medical Licensing Examination (COMLEX-USA). The Federation of State Medical Boards (FSMB) and the National Board of Medical Examiners NBME® or the National Board of Osteopathic Medical Examiners work together to co-sponsor the USMLE and the COMLEX (Shi & Singh, 2015).
Figure 3
Physician Job Tasks
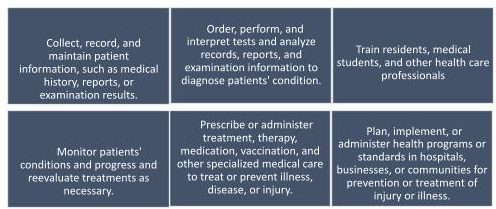
As of 2020, there were 917,940 MDs and 100,379 DOs practicing in the US and the District of Columbia, which is a 20% increase since 2010. The median salary for these physicians is $207, 380 with a slow projected growth of 1%-5% between 2020 and 2030 (BLS, 2020). These doctors are employed in a variety of settings such as hospitals, government agencies, public health departments, community centers, schools/universities, prisons, private and group practice, ambulatory care settings, and diagnostic imaging centers. Additionally, the spread of COVID 19 has necessitated that doctors deliver healthcare services through telemedicine (Young, Chaudhry, Pei, Arnhart, Dugan, Simons, 2021).
Nurse Practitioner
Nurse practitioners (NPs) are nurses who have completed education and training at the graduate level (master’s or higher) to perform in roles similar to that of a doctor including prescribing medication. Nurse practitioners serve as primary care providers in the following roles: family medicine (FNP), pediatrics (PNP), adult care (ANP), acute care (ACNP), or geriatrics (GNP). They can also work in acute care and gynecologic practices to address women’s health care including family planning, common concerns and routine screenings (Weisen, 2021). Nurse practitioners can practice independently wherein they can make decisions concerning their practice and set their work schedule and pay scale.
The NP evaluates, diagnose, treat acute and chronic illnesses, manage complex medical conditions, prescribe medications, perform surgeries including obstetrical/gynecological procedures such as delivering babies or performing cesarean sections, and provide health assessments and counseling (EveryNurse, 2021). They also educate patients regarding prevention of illnesses. Evaluation, diagnosis, and treatment are accomplished through a comprehensive assessment followed by ordering and interpreting diagnostic tests such as laboratory and radiologic that are helpful in providing a diagnosis for the patient. Treatment may comprise of non-pharmacological or pharmacologic measures. The NP utilizes holistic care through the use of other professionals such as physical therapy, occupational therapy, palliative care, or other services as needed to meet the patient’s healthcare needs (Weisen, 2021).
Nurse practitioners in most states must complete a Master of Science in Nursing (MSN) or doctoral degree program, along with advanced clinical training that exceeds their initial preparation to become a registered nurse (RN). Additionally, they must successfully pass a national certification exam to be recognized as a NP. The NP must participate in clinical evaluations and periodic peer review. Clinical competency is required and achieved through continuing education courses (EveryNurse, 2021).
According to the American Association of Nurse Practitioners (2021), greater than 325,000 Nurse Practitioners (NPs) are licensed to practice in the United States. Almost 89% of NPs are licensed to practice in primary care. Over 1 billion patients visit nurse practitioners each year. The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics predicts a continuing growth rate of 45% through the year 2030 (EveryNurse, 2021). The average salary for a NP is $111, 680.
Physician Assistant
The idea of a physician assistant materialized in 1967 in efforts to address the physician shortage. The PA would be an extension of the physician and could perform the same primary care duties (Cawley, 1991). They, like the Nurse practitioner, work under the auspices of the physician. Physician Assistants (PAs), like physicians are medical professionals who diagnose and treat illnesses (Kulo, Fleming, Gordes, Jun, Cawley, & Kayingo, 2021). Many of these professionals serve as the patient’s principal healthcare provider in the rural sector (Kulo et al, 2021). PAs perform the following services: obtain medical history, perform physical examination request and interpret laboratory and imaging tests, render diagnoses, prescribe medication, assist in surgery, and perform a wide range of therapeutic services (Merkle, Ritsema, Bauer, & Kuilman, 2011). PAs are educated at the master’s level and undergo 2000 clinical hours. This is a 2-year program beyond the bachelor’s degree (GKEN 2009). Licensing requires graduation from an accredited PA program and passing a certification exam. PAs maintain their certification by completing 100 hours of continuing education every 2 years and they must recertify every 10 years by taking a recertification exam (AAPA, 2021).
There are more than 150,000 PAs practicing in the U.S. today who encounter more than 400 million patient encounters annually (AAPA, 2021). The average salary for a PA is $115, 390. Job Growth is greater than average at 15% between 2020- 2030 (BLS, 2020). They practice in various health care settings. For example, 35.4% practice in hospitals, 5.2% in urgent care centers, 52.2% in outpatient offices or clinics and 7.2% in other settings such as schools or universities, rehabilitation centers, long term care, and correctional facilities. PAs practice in the following specialties: primary care, internal medicine, emergency medicine, pediatric medicine, and surgery (AAPA, 2021).
Knowledge Check Question: What is the role of a physician assistant in the healthcare system?
Answer: Physician assistants work under the supervision of a medical doctor and are trained to perform a variety of tasks, including taking medical histories, conducting physical exams, and assisting in surgery.
Knowledge Check Question: What is the primary role of a medical doctor in healthcare?
Answer: A medical doctor is responsible for diagnosing and treating medical conditions, prescribing medications, and providing overall patient care.
Knowledge Check Question: How does a nurse practitioner differ from a medical doctor?
Answer: Nurse practitioners are advanced practice nurses with the ability to diagnose and treat certain medical conditions. While they collaborate with physicians, they often have a more holistic approach to patient care.
Nursing Care
Nurses, as the largest group of healthcare professionals, play a fundamental role in health care transformation and will continue to do so as the medical industry and its affiliated professions continue to grow. A nurse will usually be the first health care professional encountered by the patient (Simons, 2017). As caregivers, they meet the physical, emotional, and mental health needs of the patient. All nurses must complete an accredited nursing education program and be licensed to practice in the state wherein they work (Shi & Singh, 2015). There are several types of nurses such as the licensed practical nurse, registered nurse, and advanced practiced nurses. Technicians also play a role in nursing care and will be discussed here.
Licensed Practical Nurse
The American Nurses Association (ANA) describes a Licensed Practical Nurse (LPN) or Licensed Vocational Nurse (LVN) as a member of the health care team who works under the supervision of as registered nurse (RN), advanced practice registered nurse (APRN) or a physician (MD) to provide basic and routine heath care. Their responsibilities include checking vital signs, administering medications, starting intravenous fluids (IVs), giving intramuscular injections, changing bandages or dressings, ensuring patients are comfortable, providing nourishment to patients, monitoring patients for signs of deterioration and reporting changes to the registered nurse or doctor.Licensed Practical Nurses must complete 1 year of education beyond high school in a board certified program in practical nursing and pass a national written certification exam. As part of the program of study, the LPN must complete several hours of clinical rotations (Shi & Singh, 2015). Entry level LPNs and vocational nurses must pass the National Council Licensure Examination for Practical Nurses (NCLEX-PN). Continuing education units are required to maintain licensure and the amount varies by state. This exam is used by the National Council of State Boards of Nursing (NCSBN) to ensure that the nurse has met requirements to practice nursing (NCSBN, 2020).According to the National Council of State Boards of Nursing (NCSBN) (2020), there were 920,655 licensed practical nurses/licensed vocational nurses (LPN/LVNs) in the United States as of October 2019. Employment of licensed practical and licensed vocational nurses is projected to grow 9% from 2020 to 2030 according to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. LPNs may work in long term care, physicians’ practices, home health, hospice care, private duty, public health, occupational health, etc. (Shi & Singh, 2015).
Registered Nurse
Registered nurses perform many health-related functions for the patients in their care. They connect the patient to the healthcare practitioner and other professionals by engaging in ongoing dialogue regarding the patient’s status. Figure 4 outlines the various tasks performed by nurses. Nurses assess patients to collect pertinent information regarding the patient’s presenting complaint. The nurse continues to collect information including the patient’s past medical history, mental status, socioeconomic status, and religion (Simon, 2017).
Figure 4
Duties of a Nurse
Education for the registered Nurse begins at the associate degree (ADN) level, which takes 2-3 years to complete. Associate degrees in nursing can be obtained at a community or junior college or university. A few hospitals continue to offer a diploma in nursing which also takes 2-3 years to complete. A nurse can also be educated at the baccalaureate level (BSN), which takes 4-5 years to complete at a college or university and at the masters level (MSN), which takes greater than 5 years to complete(Shi & Singh, 2015). See Figure 5 for the percentage of RNs with various degrees. To be licensed, the nurse has to graduate from a board approved program that includes a clinical rotation based on courses taken within the program. Entry level RNs must pass the National Council Licensure Examination for Registered Nurses (NCLEX-RN). Once licensed, the nurse must renew his/her license every 2 years. Each state has requirements regarding the number of continuing education units needed to maintain licensure. A nurse can work in another state as long as the state has entered into a compact agreement with the state of the nurse’s original license. About half of U.S. states belong to the nurse licensure compact (NursingLicensure.org, n.d.).
Figure 5
Percentage of RNs
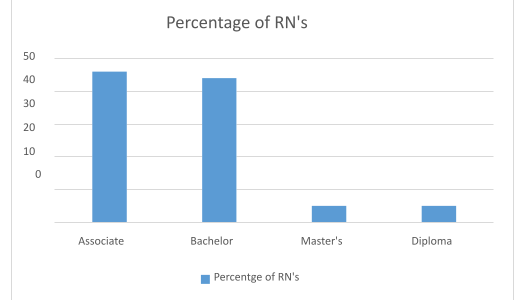
data retrieved from Registered Nurse Demographics and Statistics [2021]: Number of Registered Nurses in the US (zippia.com)
Simon (2017) reports that there are four nurses for every practicing physician or 6.2 million nurses globally with almost 60% working in medical and surgical hospitals. As of January 4, 2022, there were 5,063,470 Registered nurses licensed to practice in the U.S. (NCSBN, 2022). Registered nurses may work in hospitals, ambulatory healthcare services such as doctor’s offices, home health care and outpatient centers, nursing, long term care, and residential facilities, government, and education (Schnur, 2020).
Advanced Practice Nurses
Advanced practice nurse (APN) or advanced practice registered nurse (APRN) refers to a general classification of nurses with education, training, and clinical experience beyond the registered nurse requirements. APNs/APRNs achieve certification by a nationally recognized professional organization such as the American Nursing Credentialing Center (ANCC) in a nursing specialty or through other standards established by the Board of Nursing. Designations recognized as advanced practical nursing include clinical nurse specialist, nurse practitioner, certified registered nurse anesthetist, and certified nurse-midwife (Miller-Keane Encyclopedia and Dictionary of Medicine, 2003). All of these are classified as nonphysician practitioners (NPPs), nonphysican clinicians (NPC), or midlevel providers (MLPs). The classifications of NPP, NPC, and MLP refer to those health care professionals or physician extenders who practice in similar settings as physicians to deliver primary care but do not have a medical degree or Doctor of Osteopathic Medicine (Shi & Singh, 2015). APNs provide patient care, collaborate with other healthcare professionals, educate patients, families, and nurses, perform research, develop and implement total quality management programs (Shi & Singh, 2015). The nurse practitioner role is discussed under Overview of Primary Care Practitioners.
Clinical Nurse Specialists (CNS)
A CNS is an advanced practice nurse with a graduate level degree such as an MSN in a nursing specialty such as gerontology, pediatrics, or psychiatry. The difference between a CNS and NP is that the CNS works in a hospital while the NP works in primary care settings. The CNS performs the following duties: collect assessment data upon admission such as taking social and clinical history, ordering routine laboratory tests and radiologic examination, managing pain, managing resuscitation orders, and removing catheters. Beginning in 2010, CNSs were given the authority to practice without physician supervision in 8 states and prescribe medication and durable medical equipment in six states. Since 2016, CNSs were granted the authority to practice independently in 28 states and prescribe medication in 19 (NACNS, 2016).
Prior to certification, the CNS should hold a license to practice as a registered nurse in the state where the nurse is practicing in and hold an advanced degree at the masters, post- graduate, or doctoral level with a specialization in the field. As part of the program, the CNS must have completed an advanced physiology/ pathophysiology, advanced pharmacology, and an advanced health assessment course. In addition to the educational requirements, the CNS must have completed 500 supervised clinical hours in a CNS role in your chosen CNS field. The certification exam is run by the American Nurses Credentialing Center (ANCC) which is a part of the American Nurses Association (ANA) (RegisteredNursing.org, 2021).
According to Powers & Whitehead, (2022), about 90,000 CNSs are practicing i the United States. They are working in hospitals, clinics, private practice, schools, nursing homes, corporations and prisons with the majority of CNSs working in hospital settings. Continued growth in the number of CNS is expected for 2022 and beyond.
Certified Nurse Midwifes (CNMs)
A CNM is an advanced practice nurse who has completed a nurse-midwifery program approved by the American College of Nurse-Midwives (ACNM) and passed the ACNM National Certification Examination (Miller-Keane Encyclopedia and Dictionary of Medicine, Nursing, and Allied Health, 2003). The nurse-midwifery program of study includes topics such as maternal and fetal procedures, maternal and child nursing and assessment. The CNM can substitute for services provided by an obstetrician or gynecologist in prenatal and postnatal care. They perform services such as providing family planning education, delivering babies, and managing gynecologic and obstetric care. Patients with abnormal cases or high risk are referred to the obstetrician (Shi & Singh, 2015).
The American College of Nurse Midwives report that Certified Nurse-Midwives (CNMs) and Certified Midwives (CMs) possess an unencumbered RN license and are further educated in graduate-level midwifery programs accredited by the Accreditation Commission for Midwifery Education (ACME). CNMs and CMs pass national certification examination administered by the American Midwifery Certification Board (AMCB) to receive the professional designation of CNM or CM.
The number of midwives continues to grow. As of August 2020, there were a total of 12,990 AMCB-certified midwives in the United States of which 12,872 (99.09%) were CNMs and 118 (0.91%) were CMs (American Midwifery Certification Board, 2020). Nurse midwives work in physician and other health professional offices, outpatient care centers, colleges, universities, professional schools and government (U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, 2021).
Certified Registered Nurse Anesthetists (CRNAs)
The Certified Registered Nurse Anesthetists is an advanced practice nurse who administers intravenous, spinal, and other anesthetics during surgical operations, deliveries, and other medical and dental procedures. The CRNA has completed postgraduate training and been certified in the administration of anesthetics (Miller-Keane Encyclopedia and Dictionary of Medicine, Nursing, and Allied Health, 2003). The CRNA cares for patients requiring all types of anesthesia in various settings such as ambulatory care centers, hospitals prior to surgical procedures, on obstetric units, dentists’ offices, podiatrists’ offices, pain management, etc.
They conduct pre-anesthesia assessments and monitor the patient throughput surgery (American Association of Nurse Anesthesiology-AANA, 2022)
Obtaining CRNA education requires completion of a baccalaureate program and work in a critical care setting as a critical care nurse for 4-5 years, receiving 21-51 months of classroom instruction and clinical education and training and attain 12, 593 hours of clinical experience, including 733 hours during their baccalaureate nursing program, 9,256 hours as a critical care registered nurse, and 2,604 hours during their nurse anesthesia program. CRNAs must pass a national certification exam for entry into practice and be recertified every 4 years to remain current on anesthesia techniques and technologies. They must also pass a continued professional certification exam 8 years (AANA, 2022). As of December 2020, there were 55, 000 CRNAs in the U.S. (National Board of Certification & Recertification for Nurse Anesthetists- NBCRNA, 2022). The number of CRNAs continue to grow as noted by the AANA who reports a membership of 59,000.
Knowledge Check Question: How does the Licensed Practical Nurse and Registered Nurse role differ ?
Answer: Licensed practical nurses provide basic nursing care, such as administering medications and monitoring patient vital signs, under the supervision of registered nurses or physicians.
Knowledge Check Question: Describe the responsibilities of a registered nurse.
Answer: Registered nurses are responsible for providing patient care, administering medications, coordinating treatment plans, and educating patients and their families about health conditions and self-care.
Knowledge Check Question: What distinguishes a certified nurse midwife from other nursing roles?
Answer: Certified nurse midwives specialize in providing care to women during pregnancy, childbirth, and postpartum, emphasizing a holistic and patient-centered approach.
Knowledge Check Question: What is the role of an advanced practice nurse?
Answer: Advanced practice nurses, such as nurse practitioners and clinical nurse specialists, have advanced education and training to diagnose and manage health conditions, often working in specialized areas of healthcare.
Knowledge Check Question: What is the role of a certified registered nurse anesthetist (CRNA)?
Answer: Certified registered nurse anesthetists are specialized nurses who administer anesthesia during surgical procedures, ensuring the patient’s comfort and safety.
Technicians
A technician is an umbrella term for a healthcare professional that provides direct patient care under the supervision of a registered nurse (RN) or licensed practical nurse (LPN). They take care of the immediate need of the patient’s activities of daily living such as feeding, bathing, dressing, assisting with ambulation, keeping the patient clean and dry, etc. They take vital signs and monitor the patient’s condition and report their findings to the nurse.
Patient Care Technician (PCA)
The PCT assists with the care of patients as delegated by the RN by taking vital signs, collecting blood samples for testing, and inserting urinary catheters. The PCT also provides personal care to patients (Santiago, 2020). The Ultimate Medical Academy-UMA (2021) and Cambridge College of Healthcare Technology-CCHT (2022) provides the following duties of a patient care technician:
- Obtaining specimens, conducting tests and recording results.
- Check vital signs: blood pressure, heart rate and pulse.
- Monitoring a patient’s condition and keeping the care team updated.
- Monitoring how much a patient is eating and drinking.
- Taking patients to get x-rays or other diagnostic images.
- Obtaining specimens such a blood or urine, conducting tests and recording results.
- Deliver samples to the appropriate laboratory.
- Help patients with mobility issues get into wheelchairs.
- Help patients in and out of bed.
- Assist patients during exercise.
- Track a patient’s progress during care, including physical therapy.
- Listen to and take note of patient concerns.
- Act as a companion for patients and provide comfort.
- Serve as a liaison for family visits.
- Offer support to patients and their families during stressful or emotional times.
The PCT works in the following settings: hospitals, nursing homes, ambulatory health care services, residential care facilities, government agencies, and home healthcare services.
Training for a patient care technician is the same as for the certified nursing assistant (CNA) and takes between 9-12 months to complete. The PCT will have to pass a Prometrics exam and a certification exam supported by the National Healthcare Association. In addition to CNA certification, the PCT can seek certification as a Certified Patient Care Technician/Assistant (CPCT/A) and/or Certified Phlebotomy Technician (CPT) credentials offered through the National Health Career Association (NHA) (UMA, 2021). Currently, 1.4 million PCTs are practicing in the U.S. and the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics predicts an 8% growth for PCTs by 2030 (CCHT, 2022).
Surgical Assistant (CSA)/ Certified Surgical First Assistant (CSFA)
The CSA or CSFA is a certified professional that assists surgeons in a wide variety of surgical procedures, including orthopedic, vascular, and general surgery (Santiago, 2020). The Association of Surgical Assistants (ASA), 2021 describes a CSA as an allied health care professional who under the direction and supervision of the surgeon and in keeping with the policy of the institution, assists the surgeon with exposure, hemostasis, wound closure, and other intraoperative technical functions that will yield optimal results for the patient. As of January, 2018, The U.S Bureau of Labor Statistics approved the following classification of CSA: Based on state laws, the CSA can assist the surgeon by making incisions and closing surgical sites, manipulating or removing tissues, implanting surgical devices or drains, suctioning the surgical site, placing catheters, clamping or cauterizing vessels or tissue, and applying dressings to surgical site (CSA, 2018).
The CSA must graduate from a program accredited by the Accreditation Review Committee on Education in Surgical Technology (ARC/STSA). Initial certification as a Certified Surgical First Assistant (CSFA) requires graduation from a CAAHEP-accredited school of surgical assisting followed by satisfactory performance on the national Certified Surgical First Assistant examination. Approved continuing education is required for the CSFAs to maintain their certification or they can successfully retake the certifying examination at the conclusion of the renewal period (ASA, 2018). The National Registry for Surgical Assistants (NRSA) reports more than 4000 CSAs and CSFAs nationally and expected growth is 9% between 2020 and 2030 according to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics.
Nursing Assistant (CNA)
The duties of the Certified Nursing Assistant (CNA) are similar to those of the PCT. The CNA provides quality-of-life care such as hygiene, nutrition, safety, mobility, etc. for patients in nursing care facilities and clinics under the direction of an RN or LPN (Santiago, 2020). They also support nurses by taking vital signs, answering patient calls, and organizing supplies. Gleason (2021) provides the following list of CNA duties;
- Helping patients stay clean and comfortable
- Ensuring patient rooms are sanitary
- Assisting patients with eating and drinking
- Helping patients physically to move, such as by getting them in and out of bed or helping them change position
- Answering call buttons and other patient requests
- Taking vitals and recognizing possible warning signs, like changes in blood pressure or indications of an infected wound
- Medication administration
CNAs can work in various types of healthcare environments such as nursing homes, hospitals, rehabilitation and retirement centers, home health, government agencies. Certified nursing assistants must complete a 4-12 week state-approved training program through the American Red Cross, community colleges, hospitals, high schools, and vocational or technical colleges. Obtaining a CNA license requires successful completion of a certification exam. Zippia, 2022 reports more than 1,595,642 Certified Nursing Assistants currently employed in the United States. The Bureau of Labor Statistics estimates that the growth rate will be 8% between 2019 and 2029.
Drug Therapy or Pharmacology
While drug therapy or medications are typically prescribed by a healthcare practitioner, the patient can also obtain medications over the counter. The healthcare practitioner prescribes medications for the patient based on presenting signs, and symptoms or laboratory or radiologic results. The primary care provider (PCP) such as the dentist, podiatrist, physician, nurse practitioner, etc. writes out a prescription that the patient can take to his/her pharmacy to be filled. In lieu of hand delivering the prescription, the PCP can send the prescription to the pharmacy electronically through the electronic health record (EHR) system. Examples of medications requiring prescriptions include Zanax, Adderal, Cozaar, Atrovent, etc. Over the counter medication can be sold to the patient without a prescription. Examples of over-the-counter medications are Pepcid, Tylenol, Sudafed, etc.
Licensed Pharmacists
Pharmacists prepare and dispense medicine prescribed by the PCP, ensure the quality of medications, and maintain medication supply (GPHC, 2022). In addition, they provide consultation on the proper use of the medication including other drug or food interactions, generic drug substitutions, and major side effects. Pharmacists may also provide services such as smoking cessation, blood pressure measurement and cholesterol management (GPHC, 2022). They provide patients with education as needed and ask the patient if they have any questions regarding the medication. They also provide education to other healthcare professionals.
The pharmacists must have a license to practice pharmacy. Prior to licensure, the pharmacist must complete and graduate from an accredited pharmacy program that provides a doctorate degree in pharmacy (PharmD). They must successfully complete a licensing exam by the state board wherein they reside or wish to practice. They gain experience through an internship program provided through their program of study (Shi & Singh, 2015).
Pharmacists are employed in privately owned pharmacies, community pharmacies, or national drugstores, discount stores or department store chains. Additional places of employment for pharmacists include hospitals, managed care organizations, and pharmaceutical manufacturers (Shi & Singh, 2015).
Pharmacy Technicians
Bachenheimer (2019) describes the role of the pharmacy technician as a healthcare professional who performs routine pharmacy functions under the supervision of a pharmacist. The pharmacy technician may perform the following activities: accept prescriptions from patients and enter appropriate demographic information into the computer, review patient’s insurance information, fill and label prescriptions, collect payment, order medications from suppliers, distribute medications to patients, and monitor patients while they are taking medications. In a hospital setting the pharmacy technician may fill automated dispensing cabinets such as Pyxis MedStation medication management system. Pharmacy technicians with more advanced training may charge and credit patient accounts, mix intravenous solutions, and inventory narcotics.
At the least, a pharmacy technician must have a high school diploma. Employers in some states offer on the job training to pharmacy technicians based on the tasks to be performed.
Some employers offer pharmacy technician training courses. Formalized training can be obtained through pharmacy technicians programs offered by community and technical colleges. The programs take from 6-24 months to complete and provides the technician with a certificate or an associate’s degree. Licensure or certification requires the pharmacy technician to complete an accredited pharmacy technician program and successfully pass the certification of pharmacy technicians (ExCPT) exam (Bachenheimer, 2019). Pharmacy technicians may be employed in similar settings as pharmacists.
Knowledge Check Question: How do pharmacy technicians ensure the accuracy of prescriptions?
Answer: Pharmacy technicians verify prescription information, check for drug interactions, and measure and package medications accurately.
Knowledge Check Question: What are the typical responsibilities of a healthcare technician?
Answer: Healthcare technicians assist in various medical procedures, conduct tests, and perform routine tasks to support the work of other healthcare professionals.
Knowledge Check Question: How does a surgical assistant contribute to the operating room team?
Answer: A surgical assistant works alongside surgeons, providing support during surgical procedures, ensuring a sterile environment, and handling surgical instruments.
Knowledge Check Question: What is the role of a certified nursing assistant (CNA) in patient care?
Answer: Certified nursing assistants assist patients with daily activities, such as bathing and dressing, and provide basic healthcare services under the supervision of registered nurses.
Knowledge Check Question: What conditions does a pulmonologist treat?
Answer: Pulmonologists specialize in the diagnosis and treatment of respiratory disorders such as asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and pneumonia.
Specialty Care
Specialty care is limited to illness episodes, an organ system, or a disease process. The Patient Navigator Training Collaborative (2011) describes specialty care as the provision of ongoing or preventive care to a patient with a specific health problem or illness that requires a health care practitioner (specialist) to have detailed knowledge in the area of need. A specialist is a physician who specializes in specific health care problems. Specialists have additional education and certification for their specific specialty (Shi & Singh, 2015). Specialty care physicians are employed in a variety of settings such as hospitals, government agencies, public health departments, community centers, schools/universities, prisons, private and group practice, ambulatory care settings, and diagnostic imaging centers.
Pulmonology
Pulmonary refers to diseases that affect the lung or their involvement. It includes the chest, immune system, lungs, nose, respiratory system, and throat (Falcon, 2019). The most common lung infections are attributable to the same organisms that cause the common cold, which is a virus
Pulmonologists
Pulmonologists, also known as respiratory physicians, specialize in the health of the respiratory system and cardiopulmonary system. Pulmonary specialists study pathogens such as bacteria, viruses, and fungi that affect the human lungs. They treat noninfectious diseases such as asthma, bronchitis, emphysema, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, etc. Additionally, pulmonologists treat lung diseases caused by smoking or those caused by the environment such as pollutants, or allergens as well as those in the workplace such as paint or toxic chemicals (Falcon, 2019). They use imaging tests such as chest x-rays, CT scans, chest ultrasounds, and pulmonary function tests, sleep studies, etc. to make a diagnosis. Pulmonologists often provide care to patients needing life support and ventilation (Eske, 2020).
The pulmonologist specialty requires an undergraduate degree from a 4-year college, graduation from an accredited medical school (4-years) as well as the completion of a 3-year training in an accredited residency program in internal medicine. Following residency, a 2-3 year fellowship is required to provide further extensive training in pulmonology. They also require specialized training in critical care or sleep medicine (ONET.org, 2022; Eske, 2020). The workplace setting for a pulmonologist may include the hospital’s intensive care unit. Pulmonologists may also work as a part of a multidisciplinary practice or work in their own private practice.
Allergy and Asthma
An allergy is amplified immune reaction to substances such as pollen, foods, medications, bee stings, etc. that causes the body to release pharmacologically active chemicals leading to discomfort, tissue damage, or, in severe responses, anaphylactic shock and death (Alder, & Huang, 2020). Allergies also play a role in allergic rhinitis, urticaria, and eczema (Moragne, 1999). An allergist treats conditions and illnesses caused by allergies or related to the immune system (Shi & Singh, 2015).
Asthma is a lung disease that can present at any age and tends to run in families (Moragne, 1999). It involves chronic inflammation of the airway passages, or bronchi, which carry air into and out of the lungs. There is no cure for Asthma. However, it can be controlled with medication that reduces the inflammation and swelling that cause narrowing of the airways. Asthma sometimes can cause death. There are several environmental irritants that trigger asthma. They include infections, lung irritants such as smoke, nonsteroidal, anti- inflammatory drugs such as aspirin, weather, strenuous exercise, emotions, and allergens such as pollen, mold, dust and dust mites, cockroaches, animal dander, and food. When the asthma trigger is allergies, the condition is known as allergic asthma. Pulmonologists specialize in diseases of the lungs. Allergists are specialty physicians who treat allergies. Primary care physicians refer patients to see one of these specialists if the patient’s condition warrants specialty care (Moragne, 1999).
Immunology
Immunology refers to the body’s defense system. It is the function of the immune system or the body’s mechanism of fighting off physical, chemical, or biologic invasions. The immune system comprises cells, tissues, organs, molecules and their interactions that remove pathogens from the body. Pathogens are viruses or bacteria. The immune system can differentiate between its own cells and those of foreign or pathogenic cells and it can distinguish one foreign cell from another (Mir, 2020).
Allergists and Immunologists
As stated earlier in this discussion, an allergist treats conditions and illnesses caused by allergies or related to the immune system. An immunologists treats disorders of the immune system. Their role encompasses consulting, education, and specialists in diagnosing, treating, and managing asthma, allergic disorders, immunologic disorders, and immunodeficiency diseases (ACGME, 2021). The American Academy of Allergy, Asthma, and Immunology (2022) reports the following roles of allergists/immunologists – They treat:
- Diseases of the respiratory tract such as allergic rhinitis, sinusitis, asthma, hypersensitivity pneumonitis and occupational lung diseases
- Allergic diseases of the eye including allergic conjunctiva
- Allergic conditions of the skin including atopic dermatitis, contact dermatitis, acute/chronic urticaria or angioedema
- Adverse reactions to foods, drugs, vaccines, stinging insects and other agents
- Diseases associated with autoimmune responses to self-antigens, or auto- inflammatory syndromes
- Diseases of the immune system including primary immune deficiencies such as severe combined immune deficiency syndromes, antibody deficiencies, complement deficiency, phagocytic cell abnormalities, or other impairments in innate immunity and acquired immune deficiency related to HIV infection or drug-induced immune suppression.
- Stem cell, bone marrow and/or organ transplantation
- Gastrointestinal disorders caused by immune responses to foods including eosinophilic esophagitis or gastroenteritis, food protein-induced enteropathies
- Systemic diseases including anaphylaxis and systemic diseases involving mast cells or eosinophils
- According to The American Board of Allergy and Immunology (ABAI), candidates seeking to become an allergist or immunologists must have a valid, current, unrestricted license(s) to practice medicine in pediatrics or internal medicine or both. They must complete at least 24 consecutive months of full-time fellowship in an allergy/immunology program accredited by the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education (ACGME) or other acceptable allergy/immunology programs. Candidates are considered Board Eligible for ABAI Certification for five years after successfully completing an ACGME-approved fellowship training program in Allergy and Immunology.
Infectious Diseases
Infectious disease refers to infections affecting any part of the body. They are caused by organisms such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, or parasites. Many of these organisms are harmless and live inside and on our bodies. Some of them are even helpful. However, under certain conditions, these organisms can cause disease. Infectious diseases can be passed from person to person, from insects or animals. Others can be acquired by ingesting contaminated food or water, or exposure to environmental organisms (Healey, 2017). Of the 150 infectious diseases worldwide, viruses are responsible for 28, bacteria are responsible for 35, and protozoa are responsible for 6. Those caused by protozoa are the most serious infections. The course of history has been marked by cholera, leprosy, typhoid, typhus, plague, tuberculosis, measles, smallpox, yellow fever, and malaria (Petersen, Chen, & Schlagenhauf-Lawlor, 2011). The most current infections disease is Coronavirus 2019 (COVID 19), which is caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. It is considered a pandemic as it has spread word- wide since it began in 2019. As of the end of January, 2022; the CDC reports 74,562,066 total COVID 19 cases and 883,189 deaths in the U.S. alone. Some infectious diseases such as measles, chicken pox, or polio can be prevented through the use of vaccines. Frequent and thorough hand washing also helps protect you from most infectious diseases (Healey, 2017).
Infectious Disease Specialist
The infectious disease specialist has extensive training in internal medicine. They diagnose, treat, and manage various infectious diseases. Their focus is on the spread of disease, the body’s defense mechanism in fighting off these diseases, and how to manage and control infection. They work as primary care physicians and perform physical exams, but often accept referrals from other physicians (Matsen, 1987). The infectious disease specialist reviews a patient’s medical data, including records, X-rays and laboratory reports including blood studies and wound or body fluid cultures.
According to Ellie Williams in the Chronical, education and training for an infectious disease specialist include completion of a 4-year undergraduate degree in biology or premed, infectious disease or epidemiology followed by completion of 4 years in medical school to earn a Doctor of Medicine degree. He or she must then pass a Medical Licensing Exam. They then spend another three years studying internal medicine, often through internship and residency programs, followed by another two years training in infectious disease. They can work in private practice, governmental agencies such as the CDC and/or hospital settings.
Anesthesiology
Anesthesiology is the medical science of inducing a loss of consciousness and/or pain awareness wherein the patient experiences various degrees of muscle relaxation in body areas where procedures are to be performed such as surgery. In other words, it relieves the patient of pain during surgery. Anesthetics can be given locally such as in the shoulder, knee, wrist, or mouth, regionally such as with the spine, or generally or as a drug-induced sedation ranging from minimal to deep (Institute for Career Research, 2010.
Anesthesiologist
The anesthesiologist is a health care professional that has been specifically trained to administer anesthesia. The process begins with an evaluation of the patient prior to a surgical procedure followed by the provision of medical care before, during, and after the procedure. The anesthesiologist monitors the patient’s vital signs and level of consciousness. If the patient is admitted to the intensive care unit, the anesthesiologist coordinates and monitors the care of the patient while there including medications and special pain management techniques. The role of the anesthesiologist has expanded to the nurse anesthetists (discussed previously) and the anesthesiologist assistant (Institute for Career Research, 2010). Education and training for the anesthesiologists includes completion of 4 years of undergraduate work and an accredited college or university followed by completion of 4 years at an accredited college of medicine to become an MD and then 4 years in an anesthesiology training or residency program. Once the formal education and residency is completed, the anesthesiologists completes a written exam to become Board Certified by the American Board of Anesthesiology. If desired, the anesthesiologists can complete an additional 2 years of training in a subspecialty such as critical care management, pain management, or pediatric anesthesiology. Anesthesiologists must be licensed to practice in the state(s) in which they practice (Institute for Career Research, 2010). Anesthesiologists work in large and small hospitals, community hospitals, medical centers, freestanding inpatient and outpatient surgical centers, and pain clinics. They may also work in private and group practices, teach in medical schools, work with residents, and do research (Institute for Career Research, 2010).
Anesthesiologists Assistant (AA)
The Anesthesiologist Assistant is specifically trained to work in hospitals or medical centers under the direct supervision of an anesthesiologist. An AA performs the following tasks: collecting the patient’s health history and other preoperative information, inserting intravenous, arterial, or other special catheters, managing the patient’s airway, administering medications, adjusting anesthesia as needed, monitoring patient during surgery, and caring for the patient in the recovery room and intensive care. They may operate electronic bedside computer-based monitors and anesthesia specific laboratory functions and assist with cardiopulmonary resuscitation (Institute for Career Research, 2010).
Education includes completion of an undergraduate degree in biology, chemistry, mathematics, or physics followed by completion of an additional 24-28 month anesthesia program. Once education is completed, the AA can become certified by the National Commission for Certification for Anesthesiologist Assistant. Work settings for AAs are similar to those of anesthesiologists (Institute for Career Research, 2010).
Knowledge Check Question: What is the role of an immunologist in treating autoimmune diseases
Answer: Immunologists study the immune system and may be involved in developing treatments for autoimmune diseases by modulating immune responses.
Knowledge Check Question: What is the primary responsibility of an anesthesiologist?
Answer: Anesthesiologists administer anesthesia, monitor patients during surgery, and manage pain before, during, and after medical procedures.
Knowledge Check Question: What does an infectious disease specialist focus on?
Answer: Infectious disease specialists diagnose and treat infections caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi, or parasites.
Knowledge Check Question: What is the primary responsibility of an anesthesiologist?
Answer: Anesthesiologists administer anesthesia, monitor patients during surgery, and manage pain before, during, and after medical procedures.
Knowledge Check Question: How does an anesthesiology assistant support the anesthesiologist?
Answer: Anesthesiology assistants assist with anesthesia administration, monitor patients, and provide support to the anesthesiologist during procedures.
Cardiology
Cardiology is the diagnosis and treatment of heart disease (Farlex Partner Medical Dictionary, 2012). Another name for heart disease is cardiovascular disease or CVD. The cardiovascular system consists of the heart and its blood vessels. Four diseases are associated with CVD. Coronary artery disease (CAD) or Coronary Heart Disease (CHD) results from decreased myocardial perfusion that causes angina, myocardial infarction (MI), and/or heart failure. Cerebrovascular disease (CVD) includes diseases such as strokes and transient ischemic attacks (TIAs). Peripheral artery disease (PAD) refers to arterial disease involving the limbs that may result in decreased blood flow. Aortic atherosclerosis includes thoracic and abdominal aneurysms which are bulges in the wall of a blood vessel (Lopez, Ballard, Jan, 2021).
Cardiologist
A cardiologist is a specialty care health care practitioner who treats patients with diseases of the heart and blood vessels (Joyner, 2018). Patients are typically referred to a cardiologist if they present with cardiac problems such as a heart murmur or they have a heart attack, heart failure or cardiac arrhythmias, etc. Patients may also be referred to a cardiologist if they have a family history of heart disease, diabetes, high blood pressure, or high cholesterol. The cardiologist performs examinations, order and interpret additional tests such as echocardiogram, stress test, or heart cauterization, treats the patient with medications or other procedures such as surgery, and performs follow-up monitoring of the patient. If surgery is warranted the cardiologist refers the patient to a cardiac surgeon (Joyner, 2018).
Education and training for a cardiologist include completion of a 4-year undergraduate degree in pre-medicine, complete an additional 4 years in an accredited medical school, complete a 3-year residency program, become board certified in internal medicine, and complete a 3-year fellowship in cardiology (Joyner, 2018). The American Board of Internal Medicine (ABIM) offers certification in four subspecialties of cardiology as noted in Table 2.
|
Table 2: Cardiology Subspecialities |
||
| Speciality | Role | Education |
| Advanced Heart Failure and Transplant Cardiology | Manage advanced heart failure cases and transplant patients and implement electrophysiologic and hemodynamic support devices and perform surgical procedures. | Certification in this field require an additional year of training following a cardiovascular disease fellowship. |
| Adult Congenital Heart Disease | Manage patients who haveone or more defects in their heart or blood vessel structures. | Certification requires completing two years of additional fellowship training upon completing a cardiovascular disease fellowship. |
| Clinical Cardiac Electrophysiology | Manages complex cardiac rhythm disorders such as arrhythmias by prescribing medication, implanting electrical devices, and leveraging other international techniques. | Certification requires completion of an additional one-year fellowship after finishing a cardiovascular disease fellowship. |
| Interventional Cardiology | Involves specialized imaging and diagnostic techniques to evaluate different areas of the cardiovascular system through the use of a catheter. | Certification requires completing an additional fellowship following their cardiovascular disease training. |
| Advanced Cardiovascular Imaging | Specialize in advanced imaging. | Certification requires extensive training in Advanced Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) and Cardiovascular Computed Tomographic (CCT). |
Knowledge Check Question: What conditions does a cardiologist treat?
Answer: Cardiologists specialize in the diagnosis and treatment of heart-related conditions such as heart disease, arrhythmias, and heart failure.
Dentist
A dentist diagnoses and treats problems associated with the teeth, gums, and tissues of the mouth. Dentists prevent dental decay and gum disease through regular cleaning of patient’s teeth and teaching patients how to care for their teeth. They perform the following tasks: remove decay from teeth, fill cavities, place sealants on teeth, whiten teeth, repair cracked or broken teeth, remove teeth, administer anesthetics for painful dental procedures, prescribe antibiotics or other medications, perform and examine x-rays of the mouth (teeth, gums, jaw), make models and measurements for dental appliances (Shi & Singh, 2015).
Educational requirements include completion of a bachelor’s degree, graduation from an accredited school of dentistry to obtain a Doctor of Dental Surgery (DDS) or a Doctor of Dental Medicine (DDM) degree and pass a written and practical examination. Several specialties are offered by the American Dental association which require an additional 2-4 year residency in the area of specialty: orthodontics who straighten teeth, oral and maxillofacial surgery who performs oral surgery, pediatric dentistry, periodontics who treats the gums, prosthodontics who makes dental prostheses such as dentures, endodontics who perform root canals, public health dentistry, and oral pathology who treats diseases of the mouth. Dentists much be licensed to practice in the state in which they work. Dentists work in private or group practice, community or public health centers, the armed forces, or hospitals (Shi & Singh, 2015).
Dental Hygienist
Dental hygienists work in dental offices to provide dental care such as cleaning the teeth and education to patients such as proper dental care. They remove plaque from and polish the teeth. Dental hygienists also take and review the patient’s health record, take and develop dental x-rays and keep track of patient care, treatment plan, and schedule follow-up appointments (Shi & Singh, 2015).
Educational requirements include graduation from an accredited dental hygiene school. The dental hygienist must complete a 3-year associate degree program. They must be licensed to practice in the state wherein they work. To be licensed, the hygienist must successfully pass a national written examination and a state or regional clinical examination. Most dental hygienists work in dental offices (U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, 2021).
Dermatology
Dermatology is the branch of medicine concerned with the study of the skin, diseases of the skin, and the relationship of cutaneous lesions to systemic disease (Farlex Partner Medical Dictionary, 2012). It includes both surgical and nonsurgical treatment.
Dermatologist
The American Board of Dermatology (2022) describes a Dermatologist as a physician who examines, diagnoses, treats through mediations, injections, and surgery, and manages disorders of the hair, skin, nails and mucous membranes. They treat both children and adults. Types of diseases managed by dermatologists include skin tumors and cancers, melanomas, moles, contact dermatitis, and inflammatory skin disorders. Perform and interpret biopsies and perform surgical procedures.
Education for a dermatologist includes four years obtaining a bachelor’s degree, four years of medical school to become an MD, a one-year internship, and 3 years if residency encompassing 12,000-16,000 hours of working with patients. After residency, the dermatologists must complete a written examination given by the American Board of Dermatology, the American Osteopathic Board of Dermatology, or the Royal College of Physicians and Surgeons of Canada to become board certified (American Academy of Dermatology, 2022). Dermatologists work in physician’s offices, at hospitals or clinics, academia, or at research and science facilities. The Bureau of Labor statistics predicts a 3% growth for all physicians and surgeons between 2020 and 2030.
Endocrinology
The Society for Endocrinology describes endocrinology as the study of hormones. It is the branch of medicine that deals with the endocrine system. Survival without hormones is difficult because they control an individual’s temperature, sleep, mood, stress, growth, sugar regulation, digestion, puberty, metabolism, the reproductive system, etc. Individuals who develop hormonal irregularities may develop diseases such as diabetes, thyroid issues, pituitary, sexual, or neurological problems, obesity or cancer.
Endocrinologists
According to the American Association of Clinical Endocrinology (AACE), an endocrinologist is a physician who specializes in the field of endocrinology. Endocrinologists diagnose and treat a wide range of conditions affecting the endocrine system, including diabetes mellitus, thyroid disorders, osteoporosis, growth hormone deficiency, infertility, cholesterol problems, hypertension, obesity, etc. Their job is to ensure communication between the body systems by correcting hormonal imbalances. If you have a medical condition relating to hormonal imbalance, your primary care physician may refer you to an endocrinologist for further management of the disease.
Educational requirements for an endocrinologist include completion of a 4-year bachelor’s degree, followed by completion of a 4-year school of medicine degree to become an MD or DO, 3 years of residency training and 2-3 years of fellowship training. To become licensed and certified, the endocrinologists must have a state issued license to practice and a board certification in internal medicine and endocrinology. M.D.s must pass the United States Medical Licensing Exam (USMLE), a 3-part exam that tests a doctor’s knowledge of human anatomy and medicine. D.O.s must pass the Comprehensive Osteopathic Medical Licensing Examination (COMLEX-USA). The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) doesn’t provide individual job outlook information for endocrinologists. However, there are 8,377 endocrinologists in the US as of March of 2021 (Statista, 2021).
Knowledge Check Question: How can dentists address tooth decay?
Answer: Dentists may use procedures such as dental fillings, crowns, or root canals to address tooth decay and preserve oral health.
Knowledge Check Question: What does a dental hygienist do during a routine dental cleaning?
Answer: Dental hygienists clean teeth, remove plaque and tartar, apply fluoride, and educate patients on proper oral hygiene.
Knowledge Check Question: What skin conditions do dermatologists commonly treat?
Answer: Dermatologists treat conditions like acne, eczema, psoriasis, skin cancers, and other disorders affecting the skin, hair, and nails.
Knowledge Check Question: What conditions does an endocrinologist focus on?
Answer: Endocrinologists specialize in disorders related to the endocrine system, including diabetes, thyroid disorders, and hormonal imbalances.
Gastroenterology
Gastroenterology is a study of the gastrointestinal (GI) system. As such, it deals with normal function and diseases of the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, colon and rectum, pancreas, gallbladder, bile ducts and liver. It involves comprehension of knowledge of how material moves through the stomach and intestines, how nutrients are digested and absorbed into the body, how waste is removed from the system, and how the liver functions in digestion. Gastroenterology comprises conditions such as colon polyps and cancer, hepatitis, gastroesophageal reflux (heartburn), peptic ulcer disease, colitis, gallbladder and biliary tract disease, nutritional problems, Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS), and pancreatitis (American College of Gastroenterology, 2021).
Gastroenterologist
A gastroenterologist manages diseases of the digestive system or the GI tract and the liver. They evaluate patients with gastrointestinal complaints, treat a broad range of conditions, and provide recommendations to maintain health and prevent disease. Gastroenterologists perform endoscopies which involves the use of a lighted tube to visualize the inside of the intestinal track. They also prescribe and administer medication, perform biopsies, remove polyps from the colon, dilate or stretch narrowed areas of the esophagus or intestines, perform procedures such as hemostasis to stop bleeding and interpret test results. Societies that oversee training and education for gastroenterologists include the American Board of Internal Medicine, the American College of Gastroenterology, the American Gastroenterological Association, and the American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ACG, 2021). Examines patients to determine the nature and extent of problems after referral from general medical practitioners and other medical specialists and undertakes laboratory tests and diagnostic procedures.
Educational requirements include completion of a 4-year bachelor’s degree program and 4-year school of medicine program to become an MD. The gastroenterologist then completes a three-year Internal Medicine residency and is then eligible for additional specialized training (fellowship) in Gastroenterology, which is an additional 2-3 years. They work in hospitals or private or group practice (ACG, 2021).
General Surgery
General surgery is a holistic approach to surgery wherein the knowledge base centers on anatomy, physiology, metabolism, immunology, nutrition, pathology, wound healing, shock and resuscitation, intensive care, and neoplasia (Timmerman, 2022). It is the treatment of injury, deformity, and disease using operative procedures when medications have been unsuccessful in remedying the patient’s condition or complaint. Simple surgeries such as a vasectomy can be performed in a doctor’s office whereas removal of a gallbladder is performed in a hospital operating room setting.
General Surgeon
The general surgeon has obtained knowledge that allows diagnosis and management of the patient preoperatively, operatively, postoperatively. They also manage patients with trauma including musculoskeletal injuries and care for critically ill patients with underlying surgical conditions (Timmerman, 2022). The general surgeon demonstrates knowledge and experience in conditions affecting the alimentary tract, abdomen wall and its contents, breast, skin and soft tissue, endocrine system, surgical critical care, surgical oncology, and trauma (The American Board of Surgery, 2021)
Educational requirements for a general surgeon include completion of a 4-year bachelor’s degree, followed by completion of a 4-year school of medicine degree to become an MD or DO, 5 years of residency training. The general surgeon program must be accredited by the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education (ACGME) or The Royal College of Physicians and Surgeons of Canada (RCPSC) (The American Board of Surgery, 2022). The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) doesn’t provide individual job outlook information for general surgeons but indicates that the outlook for physicians and surgeons is expected to grow by 3 percent.
Hematology
John Hopkins Medicine describes hematology as the study of blood and blood disorders. Hematological tests can help diagnose anemia, infection, hemophilia, blood-clotting disorders, and leukemia. The Medical Dictionary for the Health Professions and Nursing (2012) further defines hematology as a medical specialty that pertains to anatomy, physiology, pathology, symptomatology, and therapeutics related to the blood and blood-forming tissues. It involves treating diseases that affect the production of blood and its components such as blood cells, hemoglobin, blood proteins, bone marrow, platelets, blood vessels, spleen, and coagulation. Diseases associated with the study of hematology include hemophilia, blood clots, bleeding disorders, leukemia, multiple myeloma, and lymphoma.
Hematologist
A hematologist evaluates, diagnose, and manages patients with blood disorders, and disorders of the bone marrow and lymphatic system. They treat nonmalignant blood disorders which include bleeding and clotting problems (such as hemophilia and pulmonary embolism) and diseases of red blood cells (such as sickle cell anemia and thalassemia). Hematologists also treat malignant blood disorders such as various leukemias and lymphomas. Diseases treated by hematologists may be caused by genetic factors, medications, patient lifestyle or environmental factors. Hematologists treat patients of all ages. They may serve as consultants to physicians and to hospitals in areas including trauma, neurosurgery, and cardiovascular disease.
Hematologists also screen for blood diseases and can offer preventive services (FREIDA: AMA, 2022). The educational path for a hematologist includes four years at the undergraduate level, four years of medical school, three years of residency in internal medicine or pediatrics, and two to four years of fellowship to specialize in hematology, pediatric hematology or oncology, or pathology (American Society of Hematology, 2021). Hematologists work primarily in hospitals.
Urology
Urology is the branch of medicine that deals with the physiology and disorders of the urinary system (kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra) and the male genitourinary tract and the female urinary tract. Urologists may also study disorders of the adrenal glands, which are closely associated with the kidneys (Alder, 2019). It also deals with the male fertility tract (penis, scrotum, testes, and prostate).
Urologist
A urologist is a medical doctor who specializes in treating diseases of the urinary tract and reproductive organs of males, females, and children. Urologists may treat and diagnose patients experiencing issues with their adrenal glands, kidneys, bladder, urethra, as well as reproductive organs. Common conditions that are treated by urologists include frequent urinary tract infections, urinary incontinence, kidney stones, hematuria (blood in the urine) and cancers of the bladder, kidneys, male infertility, and prostate (ONET.org, 2022, Alder, 2019).
To become a urologist, completion of a 4-year college degree, graduation from an accredited medical school as well as the completion of an accredited residency is required. Urologists must obtain a medical license, but a board certification is optional. The work setting for urologists may include a hospital setting or private clinic in addition to institutional settings such as hospitals or university medical centers (ONET.org, 2022).
Knowledge Check Question: What gastrointestinal conditions do gastroenterologists treat?
Answer: Gastroenterologists treat conditions such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), and liver disorders.
Knowledge Check Question: How do general surgeons collaborate with other specialists?
Answer: General surgeons often collaborate with specialists like oncologists, gastroenterologists, and urologists to provide comprehensive patient care.
Knowledge Check Question: What conditions are addressed by hematologists?
Answer: Hematologists specialize in blood-related disorders, such as anemia, leukemia, and clotting disorders.
Knowledge Check Question: What conditions do urologists treat?
Answer: Urologists focus on conditions affecting the urinary tract and male reproductive system, including kidney stones, prostate issues, and infertility.
Nephrology
Nephrology is the study of kidney disorders. Kidney disease affects 37 million adults in the United States. One hundred thousand people are on the kidney transplant list. The kidneys perform the following functions: assists in the removal of waste and excess fluid, filters the blood, controls the production of red blood cells, make vitamins that control growth, regulate blood pressure, helps regulate certain nutrients such as calcium and potassium (National Kidney Foundation, 2015). Diabetes and high blood pressure, or hypertension, are responsible for two-thirds of chronic kidney disease cases. Other causes of kidney disease include glomerulonephritis which causes inflammation and damage to the kidney’s filtering units, inherited disease such as polycystic kidney disease which causes large cysts to form in the kidneys and damage the surrounding tissue, birth defects of the kidneys or urinary tract, autoimmune diseases that occurs when the immune system turns against the body, or obstructions such as kidney stones or tumors (National Kidney Foundation, 2015).
Nephrologist
A nephrologist is a physician who specializes in the care and treatment of kidney disease. Procedures a nephrologist may perform include native kidney and transplant kidney biopsy, dialysis access insertion (temporary vascular access lines, tunneled vascular access lines, peritoneal dialysis access lines), fistula management (angiographic or surgical fistulogram and plasty), and bone biopsy. Bone biopsies are now unusual (AMA, 2022).
Nephrologists may provide care to people without kidney problems and may work in general/internal medicine, transplant medicine, immunosuppression management, intensive care medicine, clinical pharmacology, perioperative medicine, or pediatric nephrology. Nephrologists may further sub-specialize in dialysis, kidney transplantation, chronic kidney disease, cancer-related kidney diseases (Onconephrology), procedural nephrology or other non- nephrology areas as described above (AMA, 2022).
Educational and training requirements for a nephrologist include completion of a 4- year undergraduate degree and a 4-year medical school program. They may specialize in internal medicine or pediatric medicine. In the United States, after medical school adult nephrologists complete a three-year residency in internal medicine followed by a two-year (or longer) fellowship in nephrology. Complementary to an adult nephrologist, a pediatric nephrologist will complete a three-year pediatric residency after medical school or a four-year Combined Internal Medicine and Pediatrics residency. This is followed by a three-year fellowship in Pediatric Nephrology. Once training is satisfactorily completed, the physician is eligible to take the American Board of Internal Medicine (ABIM) or American Osteopathic Board of Internal Medicine (AOBIM) nephrology examination. Nephrologists must be approved by one of these boards. To be approved, the physician must fulfill the requirements for education and training in nephrology in order to qualify to take the board’s examination. If a physician passes the examination, then he or she can become a nephrology specialist. Typically, nephrologists also need two to three years of training in an ACGME or AOA accredited fellowship in nephrology (ACP, 2021).
Neurology
Neurology is the branch of science that deals with various parts of the nervous system such as central, peripheral and their subdivisions the autonomic and somatic nervous systems including their coverings, blood vessels, and all effector tissue, such as muscle. Clinical neurology is concerned with the diagnosis and treatment of disorders of the nervous system (Farlex Partner Medical Dictionary, 2012).
Neurologists
A neurologist has studied the brain and nerves and is responsible for examining and treating patients who experience illnesses and disorders of the nerves, brain, and spinal cord. They develop and manage patient treatment plans and prescribe medications for illnesses such as seizures, encephalitis, and Alzheimer’s disease (American Board of Medical Specialists, 2022). They analyze test and image data to inform diagnosis and treatment including medication (ONET, 2022).
Educational requirements and training include a degree from a 4-year college, passing the MCAT exam, graduating medical school, completing a residency program and fellowship as well as board certification. Neurologists may work in a variety of healthcare settings including private practice, healthcare clinics, hospitals, and/or universities conducting research. Salary for these physicians is $208, 000 annually (ONET.org).
Knowledge Check Question: What does a nephrologist specialize in?
Answer: Nephrologists specialize in the diagnosis and treatment of kidney disorders, including chronic kidney disease and kidney failure.
Knowledge Check Question: What conditions are treated by neurologists?
Answer: Neurologists address disorders of the nervous system, including epilepsy, migraines, and neurodegenerative diseases like Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s.
Obstetrics/Gynecology
Obstetrics and gynecology encompass management of the care of pregnant women including office visits and labor and delivery, gynecologic care, oncology, primary health care for women and related surgery. It also entails the diagnosis and treatment of issues specific to women such as breast cancer, reproductive disorders, and cervical cancer (American College of Surgeons, 2022). The difference between obstetrics and gynecology is that an obstetrician performs medical and surgical care of women before, during, and after a woman gives birth. In other words, they take care of women during their pregnancy and delivery. A gynecologist manages women’s bodies and reproductive health including diagnosis, treatment, and care of the reproductive system and breasts (UCLA, 2018).
Obstetricians/Gynecologists (OB/GYN)
These physicians diagnose and treat issues related to the medical and surgical care of the female reproductive system and associated disorders. Obstetricians and gynecologists typically work in hospitals, clinics, birthing facilities, and/or private practice. Private practice typically consists of office hours two to four days a week, surgery one to one- and one-half days a week, and management of labor and delivery (AMOG, 2022).
Required education and training for OB/GYN physicians include a degree from a 4-year college, pass MCAT exam, attend medical school, and complete a residency program. Resident education in obstetrics-gynecology must include four years of accredited, clinically oriented graduate medical education, which must be focused on reproductive health care and ambulatory primary health care for women, including health maintenance, disease prevention, diagnosis, treatment, consultation, and referral (AMOG, 2022).
Oncology
Oncology is the study of the cause, development, and treatment of tumors. The greatest concern for oncologists is malignant or cancerous tumors as they are challenging and life threatening (Shuman, 2019). Cancer can affect any organ system and affects a large proportion of the global population. Furfari (2017) reports more than 15 million new cancer cases worldwide and a corresponding 12 million cancer-related deaths.
Oncologists study how cells mutate into malignancies in efforts to prevent the continued occurrence. The primary goal for an oncologist is to evaluate, eliminate, or reduce the size of a malignancy. However, an equally important goal is to reassure the patient and their families and provide treatment to reduce pain and make the patient comfortable.
Oncologists perform biopsies of the tumor, tumor resections or surgical removal and administer radiation and chemotherapy. They also work with a range of healthcare professionals including radiologists and pathologists to provide comprehensive care to cancer patients (Shuman, 2019).
Education and training requires the completion of a 4-year college degree, 4 years of training at an accredited medical school, and residency encompassing two-four years at a board-certified cancer center. After residency, the oncologist can become certified in surgery, pediatrics or radiology. Certification is granted by such regulatory agencies as the Accreditation Council of Graduate Medical Education, the American Board of Radiology, and the American Board of Pediatrics (Shuman, 2019). Oncologists typically work in cancer clinics, medical and surgical hospitals, and outpatient cancer care centers.
Ophthalmology
Ophthalmology is a branch of medical science dealing with the structure, functions, pathology, and treatment of diseases of the eye such as cataracts, glaucoma, macular degeneration, diabetic retinopathy, etc. (American Academy of Ophthalmology, 2022). It includes any associated neurological systems that relates to vision any conditions affecting the eye and the skills and techniques used to treat eye conditions (Collins Dictionary of Medicine, 2005).
Ophthalmologist
The American Academy of Ophthalmology (2022) defines an ophthalmologist as a physician specializing in eye and vision care. They diagnose and treat all diseases of the eye, perform surgery and can correct vision through the prescribing and fitting of eyeglasses and contact lenses. The ophthalmologist can also make referrals to medical doctors for further diagnoses of medical conditions that may be causing vison or eye problems.
Becoming an ophthalmologist requires a 4-year degree, completion of a medical degree at an accredited medical school, completion of a residency program in ophthalmology, followed by an internship. A certification in Ophthalmology from the American Board of Ophthalmology is not required but highly recommended (ONET.org). Ophthalmologists may work in hospitals, Lasik centers and/or private practices.
Orthopedics
Orthopedics is the study of prevention and treatment of disorders of the skeleton, joints, muscles, and connective tissues. It is related to the moving parts of the body such as the musculoskeletal system, bones, hands, feet, hips, knees, legs, joints, ligaments, muscles, tendons, spine, and nervous system and diseases affecting them. The nervous system, skeletal system, and muscular system helps us perform activities such as walking, exercising, maintaining posture, and performing manual labor (Wallace & Fallon, 2019).
Orthopedists
Orthopedists focus primarily on the prevention and treatment of disorders of the skeleton and muscles. They maintain expertise on the development of these systems throughout the aging process (Wallace & Fallon, 2019). Orthopedists are doctors who specialize in diagnosing and correcting deformities of the musculoskeletal system, including bones, joints, tendons, ligaments, and muscles. Orthopedics is a branch of medicine that focuses on treating issues of the musculoskeletal system. Orthopedists may also help prevent orthopedic issues and may use both surgical and non-surgical treatments for musculoskeletal issues such as joint pain, back pain, and sports related injuries (ONET.org).
The orthopedist specialty requires a degree from a 4-year college, graduation from an accredited medical school as well as the completion of 5 years of training in an accredited orthopedic residency program. Orthopedists may work in a hospital setting or private clinic but most work alongside an orthopedic team that may include athletic trainers, nurse practitioners, physical or occupational therapists (ONET.org).
Knowledge Check Question: How do gynecologists contribute to women’s health?
Answer: Gynecologists address a range of women’s health issues, including reproductive health, contraception, and the management of gynecological conditions.
Knowledge Check Question: What conditions do ophthalmologists treat?
Answer: Cancer treatment plans are individualized and may include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, immunotherapy, or a combination, depending on the type and stage of cancer.
Knowledge Check Question: What types of musculoskeletal conditions do orthopedists treat?
Answer: Ophthalmologists treat conditions such as cataracts, glaucoma, macular degeneration, and perform eye surgeries.
Otorhinolaryngology
Otorhinolaryngology is the study of diseases of the ear nose and throat (ENT) (Shuman, 2019). These structures are related to the ability to take in food and air and are directly connected to speech, smell, taste, hearing, and balance. Dysfunction of the ears, nose, or throat can affect the physical, emotional, and social wellbeing of a person. Conditions and diseases associated with otorhinolaryngology include “cleft lip and palate deformities (which are often treated as well by plastic surgeons); thyroid tumors (which are also treated by oncological surgeons); skin cancers (which also fall within the practices of plastic surgeons and oncological surgeons); face lifts, the treatment of facial lacerations, and other reconstructive surgery (which plastic surgeons also handle); lumps on the salivary glands (which are sometimes treated by oncological surgeons); and jaw injuries, including fractures (which are treated by maxillofacial surgeons, many of them board-certified in otorhinolaryngology)” (Shuman, 2019, para. 4).
Otorhinolaryngologist
Otolaryngologists diagnose and treat conditions of the ear, nose, head, and throat. These doctors will examine and provide non-surgical and/or surgical treatment for the treatment of hearing loss, speech loss, ear and sinus infections, ear noise (tinnitus), nerve pain, facial and cranial nerve disorders, and injuries to the larynx. Otolaryngologists also manage congenital disorders of the outer and inner ear. These physicians may use endoscopes while the patient is under mild anesthesia to examine a patient. Additionally, magnifying devices and cameras assist physicians to examine the ears, nose, and throat and create color images to aid in making accurate diagnoses (Shuman, 2019).
Becoming an otolaryngologist typically requires a degree from a 4-year college, another 4 years of medical school, a residency program specializing in the field as well as a fellowship or specialized training program in otolaryngology and passing the American Board of Otolaryngologist exam. The work setting for Otolaryngologists typically includes a private medical or hospital-based office. They may also work in hospitals, medical university systems, or have their own medical practice (ONET.org).
Psychiatry
Psychiatry is a medical field concerned with the diagnosis, epidemiology, prevention, and treatment of mental, behavioral, and emotional problems. Patients may visit a psychiatric for a variety of reasons such as panic attacks, auditory or visual hallucinations, suicidal thoughts, depression, anxiety, etc., that disrupts their day-to-day functioning (American Psychiatric Association, 2022).
Psychiatrist
A Psychiatrist is a medical doctor who possess training to treat mental health and substance abuse disorders. Psychiatrists must be able to observe behaviors and be knowledgeable regarding other factors such as nutritional, physical or situational that may contribute to mental or emotional challenges (Piotrowski, 2019). Some of the disorders treated by psychiatrists include panic attacks, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, depression, etc.
Becoming a psychiatrist typically requires a degree from a 4-year college in biochemistry, community mental health, genetics, neurology, neuropathology, psychopathology, psychopharmacology, and social science. They complete medical school, a four-year residency in psychiatry, and two or more years of specialty residency. Specialty residencies focus on particular treatment methods (such as psychoanalysis) or methods of diagnosis and treatment for particular groups of clients (such as children, adolescents, or elders) (Piotrowski, 2019). Psychiatrists often work in private practices; many work at community mental health centers, psychiatric hospitals, and government agencies, too. Mean annual salary for a psychiatrist is $217,000 (BLS, 2020).
Radiology
Radiology in medicine focuses on the imaging of patients to diagnose and treat diseases or other medical conditions. Medical imaging relies on the use of radiation to gain information regarding the patient. Medical imaging provides the physician with the ability to see a detailed view of the inside of the human body and obtain important information about the tissues of the body. Imaging is used to detect broken bones, follow fetal development through ultrasound, diagnose cancer through computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging, and measuring the body’s metabolic activity using positron emission tomography (Oweida, 2020).
Radiologists
A radiologist is a medical doctor specializing in the diagnosis and treatment of internal injuries using specialized medical imaging techniques such as x-rays, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), computed tomography (CT), positron emission tomography (PET), nuclear medicine, and ultrasound. A radiologist is responsible for understanding radiation safety and protection since many of the imaging techniques involve the use of radiation. These physicians will connect patients connect with doctors who recommended the patient exams and suggest further examinations or treatments. Radiologists also treat diseases by using radiation or minimally invasive, image-guided surgery (ONET.org, 2022).
Becoming a radiologist requires a degree from a 4-year college, another 4 years of medical school, and completion of a residency program specializing in radiology. Radiologists may work in a variety of medical settings including diagnostic imaging centers, clinics specializing in radiation therapy, hospitals, and private practices. Radiologists may earn an annual salary of $208,000 (ONET.org, 2022).
Knowledge Check Question: What conditions are addressed by otorhinolaryngologists?
Answer: Otorhinolaryngologists, or ENT specialists, treat conditions related to the ears, nose, throat, and head and neck areas, including sinusitis, hearing loss, and tonsillitis.
Knowledge Check Question: What disorders are treated by psychiatrists?
Answer: Psychiatrists treat a range of mental health disorders, including depression, anxiety, bipolar disorder, and schizophrenia.
Knowledge Check Question: What is the role of a radiologist?
Answer: Radiologists interpret medical imaging, including X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs, to diagnose and monitor various medical conditions.
Rheumatology
The Gale Enclopedia of Medicine (2008) defines rheumatology as “the study of disorders characterized by inflammation, degeneration of connective tissue, and related structures of the body. These disorders are sometimes collectively referred to as rheumatism”. Rheumatology is devoted to the diagnosis and management of over 100 diseases. The most common rheumatic disease is arthritis (American College of Rheumatology, 2022).
Rheumatologists
Rheumatologists diagnose, treat and manage patients with arthritis and other rheumatic diseases. These health problems affect the joints, muscles, bones and other internal organs.
Rheumatology focuses on immune-mediated pain and disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Rheumatic disorders can affect the joints, muscles, and bones leading to pain, inflammation, stiffness, and malformation. Rheumatologists consult with patients, run tests to diagnose rheumatic disorders, prescribe mediation and provide treatment of musculoskeletal and autoimmune diseases (American College of Rheumatology, 2022). Rheumatologists typically work in medical offices or clinics but may also work in private practices and outpatient clinics.
Knowledge Check Question: What conditions do rheumatologists specialize in?
Answer: Rheumatologists focus on autoimmune and inflammatory disorders affecting the joints and connective tissues, such as rheumatoid arthritis and lupus.
Non Clinical Healthcare Professionals
Non clinical healthcare professionals do not diagnose, treat, or provide direct patient care. Instead, their role is to support patient care which includes diagnosis and treatment.
Some non-clinical healthcare professionals do have contact with the patients. There are many types of non-clinical roles in healthcare. Some of them will be discussed here.
Medical Billers and Coders
Medical billers and coders are the healthcare professionals responsible for the processing of patient data to ensure healthcare providers are paid for the services they perform. Medical billers and coders are involved in the medical reimbursement cycle and work with patients and providers to optimize the revenue of the healthcare facility. The financial viability of a healthcare practice depends on the overall efficiency of the medical billing and coding team. The primary responsibilities of the medical coder are to review clinical documentation to extract and translate the proper billing information into classification systems (e.g- CPT, ICD-10). Translating the clinical information using codes helps document and summarize medical services (Best Accredited Colleges, 2021).
Medical billing involves working closely with health insurance companies to receive payment for services provided by a healthcare provider in order to ensure the healthcare practice receives proper reimbursement. Medical billers are responsible for collecting patient information, entering charges, verifying patient health coverage, securing authorizations, collecting copays, and reviewing claims to ensure procedures and diagnosis codes are accurate before submitting claims to payers (Best Accredited Colleges, 2021; ONET.org, 2022).
The medical coder assigns the corresponding codes, which illustrate the type of patient visit, the patient symptoms, the doctor’s diagnosis, and what the doctor prescribes, and then the medical biller creates a claim out of these codes using a software system. The biller then sends this claim to a health insurance company. The health insurance agency will evaluate and return the claim. The biller then evaluates this returned claim and figures out how much of the bill the patient owes, after the insurance is deducted. If the patient has an insurance plan that covers this type of visit and the treatment for this condition, then the bill will most likely be relatively low. The patient may also have a co-pay, or another form of arrangement with their insurance company. The biller considers all of this information and creates an accurate bill, which is then sent to the patient. The medical biller acts somewhat as a mediator between patients, healthcare providers, and health insurance agencies. The coder translates the medical procedures into code, the biller translates the code into a financial report, and then ensures the healthcare provider is properly reimbursed for the services rendered (Best Accredited Colleges, 2021; ONET.org, 2022).
Required Education and Training for medical billers and coders include a high school diploma and enrollment in a medical billing and coding program (Associate degree programs for medical billing and coding typically take 2 years or less to complete and will provide an educational foundation in medical terminology, coding, and information technology). Most facilities require billers and coders to earn a professional certification (the certified professional biller (CPB) or the certified professional coder (CPC) credentials). They typically work in the following settings: hospitals, outpatient care facilities, law offices, health insurance agencies, and government agencies and universities (Best Accredited Colleges, 2021; ONET.org, 2022).
Medical Transcriptionists
Medical transcriptionists turn verbal notes of healthcare providers into typed reports. They are well versed in medical terminology, anatomy and physiology, diagnostic procedures, and treatment modalities, which provides the ability to recognize and spell names of muscles, bones, procedures, etc. to provide accurate patient information to physicians and other health care workers. The documents that transcriptionists produce include discharge summaries, physical examination reports, patients’ history reports, operating room reports, consultation notes, diagnostic imaging studies, autopsy reports, and referral letters (Shniper, 2001).
A license is not required to work as a medical transcriptionist; however, an associate’s degree or certification as a Registered Healthcare Documentation Specialist (RHDS) and/or Certified Healthcare Documentation Specialist (CHDS) is preferred. Medical transcriptionists work in various settings including hospitals, doctors’ offices, medical schools, and can even work remotely if they have the necessary equipment. These professionals typically work alone at their computers listening to recordings of healthcare professionals.
Medical and Health Services Managers/Hospital Executives
Healthcare managers organize, coordinate, and manage how healthcare services are delivered to patients. They provide leadership to employees of the institution and guide the strategic direction of the organization. Healthcare managers must possess a skillset and knowledge required to run complex healthcare organizations. The following leadership competencies are described by the Healthcare Leadership Alliance (1) communication and relationship management, (2) professionalism, (3) leadership, (4) knowledge of the healthcare system, and (5) business skills and knowledge (Stefl, 2008).
All health service managers do not require a degree. For example, housekeeping managers, food service managers, maintenance managers, may be employed without a degree. However, positions such as nursing home administrators, chief financial officer, chief nursing officer, chief executive officer etc. do require a degree. A bachelor’s degree is typically the minimum requirement, but most healthcare executives have a master’s degree with a specialization in health care management. Fields of study are often in or related to the following areas: hospital management, business administration, law, finance, and accounting. Licensing and certification are not required, but certifications are available. The most recognized healthcare administration certifications are the Fellow of the American College of Healthcare Executives (FACHE), Certified Medical Manager (CMM), Certified Professional in Healthcare Information and Management Systems (CPHIMS), and Certified Professional in Healthcare Risk Management (CPHRM) (BLS, 2021). Hospital executives have to work with every department within the medical facility as well as with the surrounding community groups. They typically work in offices within the healthcare facility, hospital, nursing home or group medical practice. They also serve as spokespersons for the hospital and communicate with the media as well as local, state, and federal legislators (BLS, 2021).
Medical Receptionists
Medical receptionists serve patients by providing a welcoming and hospitable environment through pleasant greetings, scheduling appointments, and answering or redirecting patient inquiries. These professionals are also responsible for retrieving and updating patient records, collecting patient financial information, while maintaining confidentiality. Medical receptionists also keep the patient appointment scheduling running smoothly by alerting providers of patient arrivals and delays. They maintain the office equipment by reviewing inventory and placing orders. A high school diploma or GED equivalent is required to work as a medical receptionist. Medical receptionists work in any medical facility or setting that offers patient care including hospitals, doctors’ offices, laboratories, and clinics ranging from mental health to physical therapy (BLS, 2021).
Knowledge Check Question: What is the role of a medical biller and coder?
Answer: Medical billers and coders assign codes to diagnoses and procedures, ensuring accurate billing and reimbursement for healthcare services.
Knowledge Check Question: What does a medical transcriptionist do?
Answer: Medical transcriptionists transcribe audio recordings from healthcare professionals into written reports, maintaining accurate medical records.
Knowledge Check Question: What responsibilities does a healthcare manager have?
Answer: Healthcare managers oversee the operations of healthcare facilities, manage staff, create and implement policies, and ensure efficient and quality patient care.
Knowledge Check Question: What is the role of a medical receptionist?
Answer: Medical receptionists manage front-desk activities, greet patients, schedule appointments, and handle administrative tasks in a medical office.
Human Resources
Human resource (HR) associates obtain and manage the human resources records. They are responsible for retrieving and logging HR information and assisting company employees with hiring procedures. HR professionals work with their facility’s executives to identify candidates that best suit the desired skills required by the open positions. They coordinate and conduct new employee orientation, develop new hire training, implement human resources polices, and process and store new employee records. Human resource associates are required to obtain an associate or bachelor’s degree in human resources or a related field such as Business Administration. Human resource associates work in offices as well as in any medical facility or setting that offers patient care (ONET, 2022; BLS, 2021).
Health Information Technologist
Health information technologists (IT) collect, analyze, and monitor patient treatment and follow-up information. They manage electronic health record systems and secure the privacy of patient information. Health information technologists also respond to requests for medical records and authenticate legal requests and authorizations. Health information technologists also provide administrative support to the rest of the health information management staff.
Health information technologists must obtain a post-secondary certificate and/or degree in health information technology or related field such as medical coding and medical transcription. Certification is not required but certifications are available and preferred such as the Registered Health Information Technician (RHIT) and Certified Professional Coder (CPC) certificates. Health IT technologists work in a wide range of settings including health clinics, hospitals, and outpatient care facilities (ONET, 2022, BLS, 2021).
Biomedical Technician
Biomedical technicians must possess the following skills intellect, dexterity and motor coordination to manage tools, procedures and materials within the work setting. Their role is to install, maintain, calibrate, and repair biomedical equipment used to diagnose and treat medical conditions. Additionally, they teach others the proper use of equipment. They maintain their skills by reading manuals and attending seminars (Buntat, Saud, Mokhtar, Kamin, & Feh, 2016).
Employers generally prefer candidates who have an associate’s degree in biomedical technology or engineering. Depending on the area of specialization, repairers may need a
bachelor’s degree, especially for advancement. Certification is not mandatory but may be useful in ensuring competence and professionalism to the employer. Some associations offer certifications for medical equipment repairers. For example, the Association for the Advancement of Medical Instrumentation (AAMI) offers certification in three specialty areas—Certified Biomedical Equipment Technician (CBET), Certified Radiology Equipment Specialists (CRES), and Certified Laboratory Equipment Specialist (CLES). Medical technicians work in the following environments: professional and commercial equipment and supplies merchant wholesalers, hospitals; state, local, and private, ambulatory healthcare services, rental and leasing services, and health and personal care retailers (BLS, 2021).
Administrative Assistant
Administrative assistants perform and coordinate office activities such as storing, retrieving, and integrating information to distribute to organizational employees. In addition to communication, they plan and schedule meetings and appointments; organize and maintain paper and electronic files; manage projects; conduct research; and disseminate information by using the telephone, mail services, Web sites, and e-mail. They also make travel arrangements for their superiors, other staff or employees, guests, etc. Administrative assistants are supported in their role through the use of the following equipment: fax machines, photocopiers, scanners, and videoconferencing and telephone systems (BLS, 2021).
A degree is not required for entry level positions as an administrative assistant. A high school diploma is sufficient with on-the-job training. However, some employers require a bachelor’s degree in business, communications, or education. Administrative assistants work in almost every industry (BLS, 2021).
Knowledge Check Question: What are the key responsibilities of a human resource associate in healthcare?
Answer: Human resource associate’s in healthcare handle recruitment, employee relations, benefits administration, and ensure compliance with HR policies.
Knowledge Check Question: What does a health information technologist do?
Answer: Health information technologists manage and secure patient health records, implement electronic health record systems, and ensure data accuracy.
Knowledge Check Question: What is the role of a biomedical technician?
Answer: Biomedical technicians maintain and repair medical equipment, ensuring that healthcare professionals have reliable tools for patient care.
Knowledge Check Question: What tasks do administrative assistants perform in a medical setting?
Answer: Administrative assistants in healthcare handle clerical duties, manage schedules, organize files, and provide general support to the medical team.
Pharmaceutical Sales Representative
Pharmaceutical sales representatives educate, endorse, promote, and disseminate medications, medical devices or diagnostic tests to doctors, dentists, and other medical professionals. They visit medical professionals at their offices and in hospitals, providing physicians with product samples and information and discussing product benefits.
Pharmaceutical sales representative’s job is to persuade medical professionals to begin or continue prescribing their medicines. Pharmaceutical sales representatives also work for companies that specialize in providing contract sales teams to the pharmaceutical industry (Hughes, 2022).
Most pharmaceutical sales representatives begin work with a certificate through the Pharmaceutical Representative Certification (PRC) program, associate or bachelor’s degree. Pharmaceutical sales representatives visit medical professionals in their offices and in hospitals. Much time is also spent driving between appointments. Depending on the employer, a pharmaceutical sales representative may be based at their employer’s office or from their own home (BLS, 2021).
Biomedical Engineer (BME)
Biomedical engineering is a combination of biology and engineering to improve healthcare. Products of BME include prosthetics, imaging equipment, regenerative medicine, medical implants, advances in drug production, and even telecommunications. Biomedical engineers also design tools such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) machines, positron emission tomography (PET) scanners, and x-ray machines and bioinstrumentation devices that connect to the human body such as pacemakers. These devices monitor health parameters or provide a therapeutic benefit. They also develop bioMEMS that can act as sensors, analyze blood or genes, or deliver drugs at a much smaller scale than traditional devices (Vezina, 2018).
Bioengineers and biomedical engineers typically need a bachelor’s degree in bioengineering, biomedical engineering, or a related engineering field. Some positions require a graduate degree. Biomedical engineers work at medical equipment or supply manufacturers, research and development facilities, healthcare and social assistance, navigational, measuring, electromedical, and control instruments manufacturers, colleges, universities, and professional schools; state, local, and private agencies (BLS, 2021).
Medical Recruiter
A medical recruiter is a hiring specialist for the healthcare industry who screens potential job candidates, reviews resumes, perform interviews, background checks, check references, and negotiate salaries. The medical recruiter serves as an intermediary between job seekers and a healthcare organization. Performing these services requires that the recruiter
have in-depth knowledge of the organization and its purpose, goals, and needs (Best Accredited Colleges, 2021). Becoming a medical recruiter entails completion of a high school diploma and in some instances completion of a bachelor’s degree in a related field. A medical recruiter may work in health care facilities or staffing firms (Best Accredited Colleges, 2021).
Medical Device Sales Representatives
Medical devices include gloves or other protective equipment, prosthesis, or imaging machines such as MRI machines. A medical device salesperson reaches out to buyers such as hospitals, nursing homes, doctor’s offices, or dental offices to market products and secure sales contracts. These visits are achieved through appointments or by making cold calls. In addition to attracting new business, they must maintain healthy relations with existing customers (Build Central, Inc., 2021).
Becoming a medical device representative require any special certification, but in order to achieve the most success, salespeople should plan on getting at least a four-year degree in biology or engineering to become familiar with the products they will be selling. In addition, some sales representatives may consider becoming certified. The National Association for Medical Sales Representatives (NAMR) administers the Registered Medical Sales Representative certification (RMSR), a credential that rewards training in the medical device sales field. The medical device sales representative works for a medical supply manufacturer or wholesaler (Build Central Inc., 2021)
Knowledge Check Question: What is the primary responsibility of a pharmaceutical sales representative?
Answer: Pharmaceutical sales representatives promote and sell pharmaceutical products to healthcare professionals, providing information about medications and building relationships.
Knowledge Check Question: What is the role of a biomedical engineer?
Answer: Biomedical engineers design and develop medical equipment, devices, and systems to improve patient care and contribute to advancements in healthcare technology.
Knowledge Check Question: What does a medical recruiter do?
Answer: Medical recruiters are responsible for finding and hiring qualified healthcare professionals, conducting interviews, and managing the recruitment process.
Knowledge Check Question: What does a medical device sales representative do?
Answer: Medical device sales representatives sell medical equipment and devices to healthcare facilities, ensuring product knowledge and customer satisfaction.
Allied Health Professionals
According to the Association of Schools of Allied Health Professionals (ASAHP), Allied Health is defined as those health professions that are distinct from medicine and nursing. This group of individuals encompasses a broad group of people who use evidence-based practices and scientific principles to diagnose, evaluate, and treat acute and chronic diseases. They promote disease prevention and teach wellness techniques. They also establish the support of healthcare systems in various settings.
Professions that are categorized as ‘allied health’ include many non-nurse or non- physician healthcare providers. To name a few, allied health professionals consist of a multitude of working healthcare specialists which includes physicians, nurses, pharmacists, radiologist, optometrist, and cardiovascular dental hygienists, diagnostic medical sonographers, dietitians, occupational therapists, physical therapists, respiratory therapists, speech language pathologists, emergency medical personnel (EMTs, paramedics), exercise science professionals, health information technologists, health educators, counselors, and technologists and assistants. As the industry of healthcare grew and the need for technology was enhanced, organizations were desperate in hiring healthcare professional with these vital skills. All of these individuals receive specialized training which complements the work of physicians and nurses. Educational requirements can range from certificates, associates, bachelors, masters, or doctoral degrees.
According to Niles, 2020, allied health professional assist doctors and nurses with direct and indirect care. There are approximately five million allied health professionals in the United States who work in 80 professions. According to the Association of Schools of Allied Health Professionals, 2018, allied health professionals can be divided into four main categories: laboratory technologist and technicians, therapeutic science practitioners, behavioral scientists, and support services. Sometimes this field is divided into just two categories: technicians/assistants and therapists/technologist.
According to ASAHP, healthcare is 18% of the United States economy and 60% of the healthcare workforce, which is twice as high as in other countries. The future is bright for allied health professionals as jobs will grow from 15.6 million to 19.8 million from 2010-2020. The outlook for the demand for healthcare workers will grow nearly twice as fast as the national economy due to the aging population, time constraints, and limitations in learning new skills (Shi & Sings, 2019; Niles, 2020).
Physical Therapist
According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, a physical therapist (PT) aids injured or ill individuals to improve movement dysfunction and manage pain. The Occupational Information Network (ONET) is developed under the sponsorship of the U.S. Department of Labor/Employment and Training Administration. According to ONET, 2020, these healthcare professionals assess, plan, organize, and participate in rehabilitative programs that improve mobility, relieve pain, increase strength, and improve or correct disabling conditions resulting from disease or injury. Figure 6 outlines the various tasks performed by physical therapist and physical therapy technicians.
Physical therapy educational programs in the United States have increased to 271 with more than 36,799 enrolled students. Physical therapy technologist and/or therapist require more advanced training at the master’s level (2-3 years in length) or above. The doctoral degree programs take 3 years to complete (Shi & Singh, 2019).
Physical Therapy Assistant
A physical therapy assistant supports physical therapists in providing physical therapy treatments and procedures. They may also assist in the development of treatment plans, carry out routine functions and modify specific treatments in accordance with patient status. To become a physical therapy assistant or technician, educational requirements are less than 2 years of postsecondary education (BLS, 2020; ONET, 2020).
Figure 6:
Physical Therapist/Physical Therapy Assistants Responsibilities

Bureau of Labor Statistics, U.S. Department of Labor, Occupational Outlook Handbook, Physical Therapists, at https://www.bls.gov/ooh/healthcare/physical-therapists.htm (visited January 07, 2022).
All states require physical therapists to be licensed, which includes passing the National Physical Therapy Examination administered by the Federation of State Boards of Physical Therapy. After gaining experience through working in the field, physical therapist can become board certified in the specialty through the American Board of Physical Therapy Specialties.
Physical therapists seeking certification must pass an exam and complete clinical work in the specialty area (BLS, 2021).
Demand for physical therapy will continue to increase due to the large numbers of aging baby boomers. This population is more likely to experience heart attacks, strokes, and mobility related injuries that require physical therapy rehabilitation. Employment for physical therapists is projected to grow 21% from 2020-2030, which is much faster than the average for all occupations (BLS, 2021).
Audiologists
Audiology is the study of hearing, hearing loss, balance, and other disorders affecting the vestibulocochlear (8th cranial, acoustic) nerve. According to the National Center for Education Statistics (NCES), 2021, “an audiologist prepares individuals to work as both audiologists and speech-language pathologists. They specialize in services that include evaluation of hearing function to detect hearing impairment and determine its cause, selection of hearing aids, hearing aid use, training in lip reading, and maintenance of normal speech (Miller-Keane Encyclopedia and dictionary of Medicine, 2003). Includes instruction in a variety of communication disorder studies, audiology, speech pathology, language acquisition, and the design and implementation of comprehensive therapeutic and rehabilitative solutions to communications problems.” Audiologists may fit hearing aids and provide auditory training.
Many perform research related to hearing problems.
In most states audiology programs require a doctoral or professional degree, but there are a few programs that allow the individual to earn a master’s degree in audiology from an accredited university. According to Figure 7, 95% of audiologist earn a doctoral degree while
5% earn a postdoctoral degree (ONET, 2020). These individuals must also achieve certification from the national association, ASHA, as well as state licensing in order to practice audiology by the American Board of Audiology (BLS, 2021; John Hopkins Medicine, 2022).
Figure 7
Education Level for Audiologist

Bureau of Labor Statistics, U.S. Department of Labor, Occupational Outlook Handbook, Audiologists, at https://www.bls.gov/ooh/healthcare/audiologists.htm (visited January 24, 2022).
Audiologists perform many tasks and responsibilities as displayed in Figure 8. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, 2021, the median pay since 2020 is $81,030 per year and
$38.95 per hour. Approximately 800 openings for audiologists are projected each year over the next decade. Many of those openings are expected to result from the need to replace workers who transfer to different occupations or exit the labor force through retirement. (BLS, 2021)
Figure 8
Audiologist Responsibilities

Bureau of Labor Statistics, U.S. Department of Labor, Occupational Outlook Handbook, Audiologists, at https://www.bls.gov/ooh/healthcare/audiologists.htm (visited January 24, 2022).
Respiratory Therapists
A Respiratory Therapist (RT and also known as respiratory therapy practitioners RCP) is responsible for assessing, treating, and caring for neonatal, pediatric, and adult patients with breathing disorders. They assume the primary responsibility for all respiratory care modalities, including the supervision of respiratory therapy technicians. Respiratory Therapists initiate and conduct therapeutic procedures, maintain patient records, and select, assemble, check, and operate equipment. These individuals practice under the direction of a physician such as a pulmonologist (Niles, 2019). Respiratory therapists mostly work in hospitals, but they also can hold positions in clinics, schools, health departments, and many other healthcare organizations.
According to the NCES, 2021, a Respiratory Therapy program is “a program that prepares individuals, under the supervision of physicians, to assist in developing respiratory care plans, administer respiratory care procedures, supervise personnel and equipment
operation, maintain records, and consult with other health care team members. The program includes instruction in the applied basic biomedical sciences; anatomy, physiology, and pathology of the respiratory system; clinical medicine; therapeutic procedures; clinical expressions; data collection and record-keeping; patient communication; equipment operation and maintenance; personnel supervision; and procedures for special population groups.”
For the most part, a respiratory therapist must have a minimum of an associate degree as the educational requirement. Currently, many programs are now offering a bachelor’s or master’s degree as an important factor for advancement in the field. Once the respiratory
therapist has met all educational requirements, they must pass an exam to obtain their license. According to Niles, 2019, all states except Alaska and Hawaii require respiratory therapist to be licensed. The National Board of Respiratory Care (NBRC) is the main certifying body for respiratory therapists.
According to BLS, as of 2020, the median pay for a respiratory therapist was $62,810 per year and $30.20 per hour. There are 135,100 people working in the field of respiratory and the job outlook is a staggering 23%. Job opportunities are excellent for respiratory therapists with about 81% of all respiratory therapists working in a hospital (BLS, 2021).
Knowledge Check Question: Who are allied health professionals?
Answer: Allied health professionals are individuals involved in healthcare who are not physicians, nurses, or dentists, such as medical technologists, therapists, and technicians.
Knowledge Check Question: What does a physical therapy assistant do?
Answer: Physical therapy assistants work under the supervision of physical therapists, helping patients with exercises and treatments to improve mobility and reduce pain.
Knowledge Check Question: What is audiology, and what does an audiologist do?
Answer: Audiology is the study of hearing. An audiologist assesses and treats hearing and balance disorders, fitting hearing aids and providing rehabilitation.
Knowledge Check Question: What is the role of a respiratory therapist?
Answer: Respiratory therapists assess and treat patients with breathing disorders, administering respiratory treatments and providing care for individuals with lung diseases.
Speech Pathologists
According to BLS, 2021, a speech pathologist is a person who assesses and treats persons with speech, language, voice, and fluency disorders. Many speech therapists select and teach alternative communication systems. They assess, diagnose, treat, and help to prevent communication and swallowing disorders in both children and adults. Many perform research related to speech and language problems. These individuals can work in hospitals, clinics, schools, and other healthcare organizations. Figure 9 displays a speech language pathologist’s responsibility.
According to the NCES, 2021, Speech language pathologists must enroll in and complete an educational program. This program “prepares individuals to evaluate the speaking, language interpretation, and related physiological and cognitive capabilities of children and/or adults and develop treatment and rehabilitative solutions in consultation with clinicians and educators.
The speech pathology program includes instruction on the anatomy and physiology of speech and hearing, biomechanics of swallowing and vocal articulation, communications disorders, psychology of auditory function and cognitive communication, language assessment and diagnostic techniques, and rehabilitative and management therapies” (NCES, 2021).
Educational requirements for speech language pathologists include a master’s degree to a post-master’s certification. Educational requirements vary by program. For speech language pathologists, they all typically need a master’s degree; however, master’s degree programs do not require a particular bachelor’s degree for admission. Some programs at the graduate level are specialized which often include language development, age-specific speech disorders, alternative communication methods, and swallowing disorders (ONET, 2021).
Most states require speech language pathologists to be licensed; other states require registration. Licensure typically requires that the individual complete a master’s degree from an accredited program, supervised clinical experience, and passing an exam (BLS, 2021). Speech language pathologists may additionally earn a Certificate of Clinical Competence in Speech- Language Pathology (CCC-SLP). This certificate is offered by the American Speech Language- Hearing Association. Speech language pathologists can choose from a multitude of specialty certifications such as child language, fluency, or swallowing. These individuals must meet work experience requirements and pass a specialty exam to become a Board Certified Specialist (BLS, 2020). Speech Language Pathologist typically earn approximately $80,480 per year and $38.69 per hour (BLS, 2021; ONET, 2021).
According to the BLS, 2021, job duties range from the following:
Figure 9
Speech Language Pathologist Responsibilities
Bureau of Labor Statistics, U.S. Department of Labor, Occupational Outlook Handbook, Speech-Language Pathologists, at https://www.bls.gov/ooh/healthcare/speech-language-pathologists.htm (visited January 18, 2022).
Occupational Therapist
An Occupational therapist (OT) assists individuals of all ages and works to improve their ability to perform tasks in their daily living environments and in the workplace. These healthcare professionals treat the injured, ill, or disabled through therapeutic use of everyday activities (BLS, 2021). Figure 10 displays many tasks and responsibilities performed by an occupational therapist.
Figure 10
Occupational Therapist (OT) Responsibilities

Bureau of Labor Statistics, U.S. Department of Labor, Occupational Outlook Handbook, Occupational Therapists at https://www.bls.gov/ooh/healthcare/occupational-therapists.htm (visited January 18, 2022).
Educational training requires a master’s degree in occupational therapy. Some programs offer doctorate degrees. The master’s degree usually takes around 2-3 years to complete, and the doctoral degree requires 3-3.5 years of study. Both programs require fieldwork while some master’s degree programs require a minimum of 24 weeks of full-time fieldwork. Doctoral students must complete additional fieldwork of at least 14-16 weeks. Some schools also offer a dual-degree program in which the student can earn both a bachelor’s degree and a master’s degree within 5 years. Occupational therapy students must pass an examination by the National Board for Certification in Occupational Therapy to obtain a license to practice in their state and complete continuing educational requirements annually to maintain their license (BLS, 2021).
The employment outlook for occupational therapists is bright. Projected growth is 17% from 2020 to 2030, which is faster than the average for all occupations. This demand will stem from patients with autism spectrum disorder. Therapists will continue to be needed in the school setting to assist children with autism in improving their social skills and growing stronger in a variety of their daily tasks (BLS, 2021).
Medical Assistants
Medical Assistants perform administrative and certain clinical duties under the direction of a physician usually in hospitals, physician’s offices, and other healthcare facilities. This is an occupation that has both administrative and clinical roles. Administrative duties may include scheduling appointments, maintaining medical records, and billing and coding information for insurance purposes. Clinical duties may include taking and recording vital signs and medical histories, preparing patients for examination, drawing blood, and administering medications as directed by physician. According to Wolper, 2013, medical assistants are usually trained in office type functions that includes training in medical records, front desk duties, and other administrative tasks. They may have other non-administrative duties such as assessing physical conditions of patients to aid in diagnosis or treatment, cleaning medical equipment, disposing of biomedical waste in accordance with standards, and interviewing patients to gather medical information. According to Niles, (2019), physicians employ medical assistants more than any other allied health assistant.
Medical Assistants undergo a type of formal training which can last between 1-2 years. According to BLS, 2021, to be a medical assistant requires no degree at all. Some may have a high school diploma or equivalent and are allowed to learn while they are on the job. Medical assistants are not required to be certified in most states. However, employers may prefer to hire certified assistants. The American Association of Medical Assistants (AAMA) offers certification to graduates of medical assisting programs accredited by the Commission on Accreditation of Allied Health Education Programs (CAAHEP) or the Accrediting Bureau of Health Education Schools (ABHES). According to the BLS, 2020, Medical Assistants earn $35.850 per year and $17.23 per hour.
The job outlook for the medical assistant is bright. This occupation is projected to grow by 185 from 2020-2030. This need for more medical assistants is directly related to the aging baby boomer population and the COVID-19 global pandemic. This will cause more physicians to hire more assistants to perform daily clinical and routine activities (BLS, 2021).
Medical Technologist
A medical technologist is similar to a medical laboratory technician but has some important differences when it comes to tasks, responsibilities, and education. A medical technologist assists licensed health care professionals in the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of a disease. They most often do not interact directly with patients. However, their work is vital to the appropriate diagnosis, treatment, and care of patients. Medical technologists may also be called medical laboratory scientists, clinical laboratory scientists, or medical laboratory technologists. They are skilled in testing and analyzing blood, other body fluids, and tissue samples. They also operate and maintain the equipment used to analyze specimens and ensure tests are completed correctly and timely (Santiago, 2020). Other responsibilities of a Medical Technologists include conducting research to increase knowledge about medical issues, cultivating micro-organisms for study, testing, or medical preparations, and developing healthcare quality and safety procedures (ONET, 2021).
Medical technologists’ training is more extensive than that of the medical lab technicians with whom they often work. Medical technicians are limited to health care workers with access to controlled substances and with access to or contact with patients in a health care
facility or in a medical establishment. Most medical technicians assist lab professionals and technologists in the laboratory. They may also assist in collecting samples from patients, but only under the direct supervision of a medical technologist.
Education varies for medical technologist due to specialty. A bachelor’s degree is usually required for the role of conducting more complex lab tests. An associate’s degree or certificate is usually required to work as a technician. There were 33,100 medical technicians in 2020, which has grown over the past five years. This field is expected to grow even more over the next five years, likely to reach 37,800 by the year 2025 (ABS Labor Force Survey, 2020). According to BLS, 2020, medical technologists make approximately $45,620 annually. Medical technicians usually earn the most working at hospitals compared to working in outpatient care centers, medical and diagnostic laboratories, and doctor offices.
Knowledge Check Question: Speech pathologists assess and treat communication and swallowing disorders, working with individuals to improve speech and language skills.
Answer: What does a speech pathologist do?
Knowledge Check Question: What is the role of an occupational therapist?
Answer: Occupational therapists help individuals with physical, developmental, or emotional challenges regain or develop skills for daily living and work.
Knowledge Check Question: What tasks are typically performed by a medical assistant?
Answer: Medical assistants assist healthcare professionals with clinical and administrative tasks, including taking patient vitals, preparing exam rooms, and handling paperwork.
Knowledge Check Question: What is the role of a medical technologist?
Answer: Medical technologists perform laboratory tests on patient samples, analyze results, and contribute to the diagnosis and treatment of diseases.
Medical Laboratory Technicians
Medical Laboratory Technicians play key roles in diagnosing diseases, assessing the impact of the disease, collecting samples and performing tests to analyze body fluids, tissue, and other substances. Many clinical laboratory technologists and technicians work in hospitals.
Others work in medical and diagnostic laboratories or doctors’ offices (Niles, 2019). According to BLS, 2021, Clinical laboratory technologists and technicians typically do the following:
Analyze body fluids, such as blood, urine, and tissue samples, and record normal or abnormal findings
Study blood samples for use in transfusions by identifying the number of cells, the cell morphology or the blood group, blood type, and compatibility with other blood types
Operate sophisticated laboratory equipment, such as microscopes and cell counters
Use automated equipment and computerized instruments capable of performing a nu8mber of tests at the same time
Log data from medical tests and enter results into a patient’s medical record
Discuss results and findings of laboratory tests and procedures with physicians
According to the National Center for Education and Statistics (NCES), 2021, programs focused training medical laboratory technicians prepare individuals to perform routine medical laboratory procedures and tests and to apply strategies to record and analyze data. The program includes “instruction in general laboratory procedures and skills; laboratory mathematics; medical computer applications; interpersonal and communications skills; and the basic principles of hematology, medical microbiology, immunohematology, immunology,
clinical chemistry, and urinalysis.”
Education can vary for this field, according to BLS, 2021, clinical laboratory technologists usually need a bachelor’s degree. However, technicians usually need an associate’s degree or a post-secondary certificate. Also, some states do require technologists and technicians to be licensed. Coursework emphasizes chemistry, biology, microbiology, math, and statistics.
Clinical laboratory technologists and technicians can obtain general certification and licensing through the American Society for Clinical Laboratory Science.
The median annual wage for clinical laboratory technologists and technicians as of May 2020 was $54,180 per year. The lowest 10% earned less than $31,450 and the highest 10 percent earned more than $83,700 (BLS, 2021).
Dietitians
Dietitians plan and conduct food service or nutritional programs to help people lead healthy lives. They also plan and conduct food service or nutritional programs to assist in the promotion of health and control of disease. Dietitans may supervise activities of a department providing quantity food services, counsel individuals, or conduct nutritional research. Figure 11 displays many of the responsibilities of a dietitian. Dietitians and nutritionists work in many settings, including hospitals, nursing homes, clinics, cafeterias, and for state and local governments (BLS, 2021; ONET, 2021).
Figure 11

Bureau of Labor Statistics, U.S. Department of Labor, Occupational Outlook Handbook, Dietitians and Nutritionists, at https://www.bls.gov/ooh/healthcare/dietitians-and-nutritionists.htm (visited February 01, 2022).
A dietitian program should be one “that prepares individuals to integrate and apply the principles of the food and nutrition sciences, human behavior, and the biomedical sciences to design and manage effective nutrition programs in a variety of settings. Instructions in human nutrition; nutrient metabolism; the role of foods and nutrition in health promotion and disease prevention; planning and directing food service activities; diet and nutrition analysis and planning; supervision of food storage and preparation; client education; and professional standards and regulations” are also included in the program of study (NCES, 2021).
Dietitians usually need a bachelor’s degree or higher in dietetics, food, and nutrition, or any other related field to enter the workforce. They also receive training in the form of internships following graduation from college (BLS, 2021). Many states also require dietitians and nutritionists to be licensed in order to practice their skills. The RD/RDN designation is administered by the Commission on Dietetic Registration which is the credentialing agency for the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics (BLS, 2021).
The median annual wage earnings for dietitians since May 2020 was $63,090 and $30.33 per hour. The outlook is bright for dietitians due to the need for food and nutrition in promoting health and wellness and preventive care. Understanding diet can prevent and control several illnesses such as diabetes, strokes, and heart diseases (BLS, 2020)
Diagnostic Medical Sonographers
Diagnostic medical sonographers use medical ultrasound, which photographs internal structures, to provide services to patients (Niles, 2019). According to the BLS, 2021, Diagnostic medical sonographers and cardiovascular technologists and technicians, including vascular technologists operate special imaging equipment to create images or to conduct tests. These specialties gather data to assist the physician with disease management in a variety of medical settings. Medical sonographers can specialize in several healthcare areas like obstetric and gynecologic sonography, neuro-sonography, breast sonography, abdominal sonography, gall bladder, spleen, and pancreatic sonography, and cardiac sonography just to name a few (Niles, 2019). The opportunities for advancement are vast.
According to the BLS (2021), individuals interested in becoming a medical sonographer must take courses in anatomy, medical terminology, and applied sciences. Individuals must
attend a “program that prepares individuals, under the supervision of physicians, to utilize medical ultrasound techniques to gather sonographic data used to diagnose a variety of conditions and diseases. Instruction includes obtaining, reviewing, and integrating patient histories and data; patient instruction and care; anatomic, physiologic and pathologic data recording; sonographic data processing; sonography equipment operation; and professional standards and ethics” (NCES, 2021).
Niles, (2019) report that colleges and universities offer formal training in both 2- and 4-year programs which will award an associate’s or a bachelor’s degree. Some programs have a 1- year certificate program but they must have the necessary clinical experience. Diagnostic medical sonographers may earn professional certification through the American Registry for Diagnostic Medical Sonographers, Cardiovascular Credentialing International, and the American Registry of Radiologic Technologist. According to the BLS, 2021, “the median annual wage for cardiovascular technologists and technicians was $59,100 in May 2020. The median wage is the wage at which half the workers in an occupation earned more than that amount, and half earned less. The lowest 10 percent earned less than $30,140, and the highest 10 percent earned more than $96,790.”
Radiographers
Radiologic technologists perform diagnostic imaging examinations on patients. MRI technologists operate magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scanners to create diagnostic images. MRI technologists specialize in magnetic resonance imaging scanners. They inject patients with contrast media, such as a dye, so that the images will show up on the scanner. The scanners use magnetic fields in combination with the contrast agent to produce images that a physician can use to diagnose medical problems. These healthcare professionals take x-rays and CAT scans or administer nonradioactive materials into a patient’s bloodstream for diagnostic or research purposes. Includes radiologic technologists and technicians who specialize in other scanning modalities (BLS, 2021; ONET, 2021). Figure 12 displays the responsibilities of radiographers.
These individuals work in hospitals or in cancer treatment centers (Niles, 2019).
Usually a bachelor’s, associate degree, or certificate in radiation therapy is necessary to become a radiation therapist/technologist. Radiologic technologists are trained in the use of different types of medical diagnostic equipment. They may choose to specialize in x-ray, mammography, or computed tomography (CT) imaging. Some radiologic technologists provide a mixture for the patient to drink that allows soft tissue to be viewed on the images that the radiologist reviews (BLS, 2021).
Figure 12
Bureau of Labor Statistics, U.S. Department of Labor, Occupational Outlook Handbook, Radiologic and MRI Technologists, at https://www.bls.gov/ooh/healthcare/radiologic-technologists.htm (visited January 17, 2022).
Individuals who would like to become a radiology therapist/technician must enroll in a program such as a bachelor’s degree, associate degree, or certificate in radiation therapy.
Many states do require certification and licensure in this field. According to the NCES, 2021, one should enroll in a program that prepares individuals, under the supervision of physicians, to provide medical imaging services to patients and attending health care professionals. Includes instruction in applied anatomy and physiology, patient positioning, radiographic technique, radiation biology, safety and emergency procedures, equipment operation and maintenance, quality assurance, patient education, and medical imaging/radiologic services management. To become a licensed radiographer, certification is available through the American Registry of Radiologic Technologists (ARRT) (BLS, 2020).
Projected job openings in this field are 212,100 employees with a projected growth of 5- 10% for 2020-2030 (BLS, 2020). Radiology therapist/technicians can earn annually $74,690 as of May 2020. The median wage is the wage at which half the workers in an occupation earned more than that amount, and half earned less (BLS, 2020). According to ONET, (2020) the median wage was $61,900 annually and $29.76 per hour.
Knowledge Check Question: How does a medical laboratory technician differ from a medical technologist?
Answer: Medical laboratory technicians perform routine laboratory tests under the supervision of medical technologists, contributing to the analysis of patient samples.
Knowledge Check Question: What is the role of a dietitian in healthcare?
Answer: Dietitians assess and provide nutritional guidance to individuals and groups, helping manage health conditions and promoting overall well-being through diet.
Knowledge Check Question: What does a diagnostic medical sonographer do?
Answer: Diagnostic medical sonographers use ultrasound technology to create images of internal body structures, aiding in the diagnosis and treatment of medical conditions.
Knowledge Check Question: What is the role of a radiographer or radiologic technologist?
Answer: Radiographers operate imaging equipment (X-rays, CT scans, etc.) to produce diagnostic images, assisting physicians in diagnosing and treating medical conditions.
CONCLUSION
Health care continues to be the largest U.S. employer. Many types of healthcare professionals contribute to the delivery of healthcare such as primary care practitioners, specialty care practitioners, pharmacists, allied health professionals, non-clinical healthcare professionals, nurses, and various types of technicians. These healthcare professionals work in a variety of settings and require various levels of education and training based on their specialties.
Job categories in the healthcare industry will continue to grow based on predictions from the Bureau of Labor Statistics. The increased availability of insurance, aging, advances in research and technology, disease and illness trends, and population growth are increasing the need for healthcare professionals. Other forces increasing the need for healthcare professionals include improving healthcare quality, increasing access to care, and controlling healthcare costs (Shi & Singh, 2019; Zhang, Lin, Pforsich, & Lin, 2020). Although physicians play a major role in health care delivery, their presence is underrepresented, especially in the rural sectors of the United States.
Case Study: Enhancing Healthcare Delivery Through the Integration of Primary and Specialty Care
Introduction:
United Medical Center (UMC) is a leading, multi-specialty healthcare facility serving a diverse community. UMC is committed to providing comprehensive and patient-centered care to its community. Recognizing the importance of coordination between primary and specialty care, UMC leadership has initiated a strategic initiative to integrate these services. This case study explores the implementation of this integration initiative to enhance healthcare delivery and improve patient outcomes.
Case Study Scenario:
UMC is experiencing challenges in delivering coordinated care across primary and specialty services. Patients often experience fragmented care, leading to gaps in treatment and suboptimal outcomes. To address these issues, UMC’s leadership team has devised a plan to integrate primary and specialty care that included following key components of primary and specialty integration:
Shared Electronic Health Records (EHR): UMC implemented a unified EHR system accessible to all primary care physicians (PCPs) and specialty care providers. This allows for real-time information sharing, enabling better coordination and continuity of care.
Co-located Clinics: Primary care and select specialty clinics are co-located within HMC’s premises to facilitate easy access for patients and collaboration among healthcare teams. This physical integration fosters communication and streamlines referrals between primary and specialty care providers.
Multidisciplinary Care Teams: UMC forms multidisciplinary care teams comprising primary care physicians, specialists, nurses, pharmacists, and other allied health professionals. These teams collaborate closely to develop personalized care plans tailored to each patient’s needs, ensuring a holistic approach to healthcare delivery.
Care Coordination Tools: UMC utilizes care coordination tools, such as care pathways and care coordinators, to manage complex patient cases effectively. These tools help track patients’ progress, ensure timely follow-up, and prevent care gaps between primary and specialty services.
By leveraging the expertise of various healthcare practitioners UMC aims to improve patient outcomes, increase access to care, and promote continuity of care throughout patients’ healthcare journey.
Case Study Discussion Questions
Define primary care and its significance in healthcare delivery.
How does primary care differ from specialty care?
How do primary care practitioners collaborate with other healthcare professionals to ensure comprehensive patient care?
Outline the different types of nursing care practitioners commonly found in healthcare settings.
How does the integration with primary care services enhance coordination and continuity of care for patients requiring specialty services?
Case Study References:
Berenson RA, Hammons T, Gans DN, et al. A house is not a home: keeping patients at the center of practice redesign. Health Aff (Millwood). 2008;27(5):1219-1230. doi:10.1377/hlthaff.27.5.1219
Bodenheimer T, Berry-Millett R. Care management of patients with complex health care needs. Synth Proj Res Synth Rep. 2009;(19):1-31.
Institute of Medicine (US) Committee on Quality of Health Care in America. Crossing the Quality Chasm: A New Health System for the 21st Century. Washington (DC): National Academies Press (US); 2001. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK222274/
Schor EL. The future pediatrician: promoting children’s health and development. J Pediatr. 2007;151(2 Suppl):S13-S20. doi:10.1016/j.jpeds.2007.06.033
Shortell SM, McCurdy RK. Integrated health systems. Stud Health Technol Inform. 2000;77:367-381.
World Health Organization. Framework on integrated, people-centered health services. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2016. Available from: https://apps.who.int/gb/ebwha/pdf_files/EB138/B138_36-en.pdf
Key Points
The American health care system is vast, complex and powerful.
Primary Care is the patient’s point of entry or initial contact with the health care system.
As of 2020, there were 917,940 MDs and 100,379 DOs practicing in the US and the District of Columbia, which is a 20% increase since 2010.
Over 1 billion patients visit nurse practitioners each year.
Nurses as the largest group of healthcare professionals play a fundamental role in health care transformation and will continue to do so as the medical industry and its affiliated professions continue to grow.
There are four nurses for every practicing physician or 6.2 million nurses globally with almost 60% working in medical and surgical hospitals.
Specialty care is the provision of ongoing or preventive care to a patient with a specific health problem or illness that requires a health care practitioner (specialist) to have detailed knowledge in the area of need.
Many organisms are harmless and live inside and on our bodies. Some of them are even helpful.
Non clinical healthcare professionals do not diagnose, treat, or provide direct patient care.
Allied health includes many non-nurse or non-physicians healthcare providers.
Key Words
Administrative assistants perform and coordinate office activities such as storing, retrieving, and integrating information to distribute to organizational employees.
Advanced practice nurse (APN) or advanced practice registered nurse (APRN) refers to a general classification of nurses with education, training, and clinical experience beyond the registered nurse requirements. APNs provide patient care, collaborate with other healthcare professionals, educate patients, families, and nurses, perform research, develop and implement total quality management programs
Allergy is amplified immune reaction to substances such as pollen, foods, medications, bee stings, etc. that causes the body to release pharmacologically active chemicals leading to discomfort, tissue damage, or, in severe responses, anaphylactic shock and death.
Allergist: an allergist treats conditions and illnesses caused by allergies or related to the immune system.
Allied Health is defined as those health professions that are distinct from medicine and nursing.
Anesthesiology is the medical science of inducing a loss of consciousness and/or pain awareness wherein the patient experiences various degrees of muscle relaxation in body areas where procedures are to be performed such as surgery.
Anesthesiologist is the health care professional that has been specifically trained to administer anesthesia.
Anesthesiology Assistant is specifically trained to work in hospitals or medical centers under the direct supervision of an anesthesiologists.Asthma involves chronic inflammation of the airway passages, or bronchi, that carry air into and out of the lungs.
Audiology is the study of hearing, hearing loss, balance, and other disorders affecting the vestibulocochlear (8th cranial, acoustic) nerve.
Audiologist specialize in services that include evaluation of hearing function to detect hearing impairment and determine its cause, selection of hearing aids, hearing aid use, training in lip reading, and maintenance of normal speech.
Biomedical engineering is a combination of biology and engineering to improve healthcare.
Biomedical technicians install, maintain, calibrate, and repair biomedical equipment used to diagnose and treat medical conditions.
Cardiology is the diagnosis and treatment of heart disease.
Cardiologist is a specialty care health care practitioner who treats patients with diseases of the heart and blood vessels.
Certified Nurse Midwife is an advanced practice nurse who has completed a nurse-midwifery program approved by the American College of Nurse-Midwives (ACNM) and passed the ACNM National Certification Examination
Certified Nursing Assistant (CNA) provides quality-of-life care such as hygiene, nutrition, safety, mobility, etc. for patients in nursing care facilities and clinics under the direction of an RN or LPN
The Certified Registered Nurse Anesthetists is an advanced practice nurse who administers intravenous, spinal, and other anesthetics during surgical operations, deliveries, and other medical and dental procedures.
Clinical Nurse Specialist is an advanced practice nurse with a graduate level degree such as a MSN in a nursing specialty such as gerontology, pediatrics, or psychiatry.
Dentist diagnoses and treats problems associated with the teeth, gums, and tissues of the mouth.
Dental hygienists work in dental offices to provide dental care such as cleaning the teeth and education to patients such as proper dental care.
Dermatology is the branch of medicine concerned with the study of the skin, diseases of the skin, and the relationship of cutaneous lesions to systemic disease.
Dermatologists is a physician who examine, diagnoses, treats through mediations, injections, and surgery, and manages disorders of the hair, skin, nails and mucous membranes.
Diagnostic medical sonographers and cardiovascular technologists and technicians, including vascular technologists operate special imaging equipment to create images or to conduct tests.
Dietitians plan and conduct food service or nutritional programs to help people lead healthy lives.
Endocrinology as the study of hormones.
Endocrinologist is a physician who specializes in the field of endocrinology. Endocrinologists diagnose and treat a wide range of conditions affecting the endocrine system, including diabetes mellitus, thyroid disorders, osteoporosis, growth hormone deficiency, infertility, cholesterol problems, hypertension, obesity, etc.
Gastroenterology is a study of the gastrointestinal (GI) system.
Gastroenterologist manage diseases of the digestive system or the GI tract and the liver.
Generalist and medical doctor are used interchangeably to describe a graduate from a school of medicine who is a board certified, licensed practitioner who provides a broad spectrum of care within their own specialty.
General surgery is the treatment of injury, deformity, and disease using operative procedures when medications have been unsuccessful in remedying the patient’s condition or complaint.
General surgeon has knowledge that allows diagnosis and management of the patient preoperatively, operatively, postoperatively. They also manage patients with trauma including musculoskeletal injuries and care for the critically ill patient with underlying surgical conditions.
Health information technologists (IT) collect, analyze, and monitor patient treatment and follow-up information.
Healthcare managers organize, coordinate, and manage how healthcare services are delivered to patients.
Hematology is the study of blood and blood disorders. Hematological tests can help diagnose anemia, infection, hemophilia, blood-clotting disorders, and leukemia.
Hematologist evaluates, diagnose, and manages patients with blood disorders, and disorders of the bone marrow and lymphatic system.
Human resource (HR) associates obtain and manage the human resources records. They are responsible for retrieving and logging HR information and assisting company employees with hiring procedures.
Immunology refers to the body’s defense system. It is the function of the immune system or the body’s mechanism of fighting off physical, chemical, or biologic invasions.
Immunologists treats disorders of the immune system.
Infectious disease refers to infections affecting any part of the body.
Infectious Disease Specialist has extensive training in internal medicine. They diagnose, treat, and manage various infectious diseases.
Licensed Practical Nurse (LPN) or Licensed Vocational Nurse (LVN) is a member of the health care team who works under the supervision of as registered nurse (RN), advanced practice registered nurse (APRN) or a physician (MD) to provide basic and routine heath care.
Medical Assistants perform administrative and certain clinical duties under the direction of a physician usually in hospitals, offices of physicians, and other healthcare facilities. This is an occupation that has both administrative and clinical roles.
Medical billers and coders are the healthcare professionals responsible for the processing of patient data to ensure healthcare providers are paid for the services they perform.
Medical device sales person reaches out to buyers such as hospitals, nursing homes, doctor’s offices, or dental offices to market products and secure sales contracts.
Medical Laboratory Technicians play key roles in diagnosing diseases, assessing the impact of the disease, collecting samples and perform tests to analyze body fluids, tissue, and other substances.
Medical receptionists serve patients by providing a welcoming and hospitable environment through pleasant greetings, scheduling appointments, and answering or redirecting patient inquiries.
Medical recruiter is a hiring specialist for the healthcare industry who screens potential job candidates, reviews resumes, perform interviews, background checks, check references, and negotiate salaries.
Medical technologist assists licensed health care professionals in the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of a disease but who is not licensed or registered by a specific regulatory board as a medical laboratory technician.
Medical transcriptionists turn verbal notes of healthcare providers into typed reports.
Nephrology is the study of kidney disorders.
Nephrologist is a physician who specializes in the care and treatment of kidney disease.
Neurology is the branch of science that deals with various parts of the nervous system such as central, peripheral and their subdivisions the autonomic and somatic nervous systems including their coverings, blood vessels, and all effector tissue, such as muscle.
Neurologist study the brain and nerves and is responsible for examining and treating patients who experience illnesses and disorders of the nerves, brain, and spinal cord.
Non clinical healthcare professionals do not diagnose, treat, or provide direct patient care. Instead, their role is to support patient care which includes diagnosis and treatment.
Nurse practitioners (NPs) are nurses who have completed education and training at the graduate level (Masters or higher) to perform in roles similar to that of a doctor including prescribing medication.
Obstetrics and gynecology encompasses management of the care of pregnant women including office visits and labor and delivery, gynecologic care, oncology, primary health care for women and related surgery.
Obstetricians/Gynecologists (OB/GYN) diagnose and treat issues related to the medical and surgical care of the female reproductive system and associated disorders.
Occupational therapist (OTs) assist individuals of all ages and improve their abilities to perform tasks in their daily living environments and in the workplace.
Oncology is the study of the cause, development, and treatment of tumors.
Oncologists study how cells mutate into malignancies in efforts to prevent the continued occurrence.
Ophthalmology is a branch of medical science dealing with the structure, functions, pathology, and treatment of diseases of the eye such as cataracts, glaucoma, macular degeneration, diabetic retinopathy, etc.
Ophthalmologist is a physician specializing in eye and vision care.
Orthopedics is the study of prevention and treatment of disorders of the skeleton, joints, muscles, and connective tissues.
Orthopedists focus primarily on the prevention and treatment of disorders of the skeleton and muscles.
Otorhinolaryngology is the study of diseases of the ear nose and throat (ENT).
Otolaryngologists diagnose and treat conditions of the ear, nose, head, and throat.
Patient Care Technician assists with the care of patients as delegated by the RN by taking vital signs, collecting blood samples for testing, and inserting urinary catheters.
Pharmaceutical sales representatives educate, endorse, promote, and disseminate medications, medical device or diagnostic test to doctors, dentists, and other medical professionals.
Pharmacists prepare and dispense medicine prescribed by the PCP, ensure the quality of medications, and maintain medication supply
Pharmacy Technician is a healthcare professional who performs routine pharmacy functions under the supervision of a pharmacists.
Physical therapist (PT) provide assistance towards injured or ill individuals improve movement dysfunction and manage pain
Physician Assistants (PAs), like physicians are medical professionals who diagnose and treat illnesses.
Psychiatry is a medical field concerned with the diagnosis, epidemiology, prevention, and treatment of mental, behavioral, and emotional problems.
Psychiatrist is a medical doctor who possess training to treat mental health and substance abuse disorders.
Pulmonary refers to diseases that affect the lung or their involvement.
Pulmonologists, also known as respiratory physicians, specialize in the health of the respiratory system and cardiopulmonary system.
Radiologic technologists perform diagnostic imaging examinations on patients.
Radiology in medicine focuses on the imaging of patients to diagnose and treat diseases or other medical conditions.
Radiologist is a medical doctor specializing in the diagnosis and treatment of internal injuries using specialized medical imaging techniques such as x-rays, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), computed tomography (CT), positron emission tomography (PET), nuclear medicine, and ultrasound.
Registered nurses perform many health related functions for the patients in their care. Nurses assess patients to collect pertinent information regarding the patients presenting complaint. The nurse continues to collect information including the patients past medical history, mental status, socioeconomic status, and religion.
Respiratory Therapist is responsible for assessing, treating, and caring for neonatal patients with breathing disorders.
Rheumatology is the study of disorders characterized by inflammation, degeneration of connective tissue, and related structures of the body.
Rheumatologist diagnose, treat and manage patients with arthritis and other rheumatic diseases.
Specialty care is the provision of ongoing or preventive care to a patient with a specific health problem or illness that requires a health care practitioner (specialist) to have detailed knowledge in the area of need.
Speech pathologist assesses and treats persons with speech, language, voice, and fluency disorders.
Surgical Assistant (CSA)/ Certified Surgical First Assistant (CSFA) is a certified professional that assists surgeons in a wide variety of surgical procedures, including orthopedic, vascular, and general surgery
A technician is an umbrella term for a healthcare professional that provides direct patient care under the supervision of a registered nurse (RN) or licensed practical nurse (LPN).
Urology is the branch of medicine that deals with the physiology and disorders of the urinary system (kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra) and the male genitourinary tract and the female urinary tract.
Urologist is a medical doctor who specializes in treating diseases of the urinary tract and reproductive organs of males, females, and children.
References
AACE. All about Endocrinology. Retrieved January 26, 2022, from https://www.aace.com/all-
about-endocrinology/what-endocrinologist
ABS Labour Force Survey, seasonally adjusted data. (Nov. 2020). National Skills Commission. Retrieved from https://joboutlook.gov.au/occupations/medical-technicians?occupationCode=3112
ACGME. (2021). ACGME Program Requirements for Graduate Medical Education in Allergy and Immunology. Retrieved from, https://www.acgme.org/globalassets/pfassets/programrequirements/020_allergyimmu nology_2021_tcc.pdfActive RN Licenses. A Profile of Nursing Licensure in the U.S. Retrieved January 5, 2022 from, https://www.ncsbn.org/6161.htmAdvanced practice nurse. (n.d.) Miller-Keane Encyclopedia and Dictionary of Medicine, Nursing, and Allied Health, Seventh Edition. (2003). Retrieved January 6 2022 from https://medical-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com/advanced+practice+nurse
Alder, R., PhD. (2019). Urology. Magill’s Medical Guide (Online Edition).
Alder, R., PhD, & Huang, S.-W., MD. (2020). Allergies. Salem Press Encyclopedia of Health. American Academy of Dermatology. (2022). What is a Dermatologist. Retrieved January 26,2022, from https://www.aad.org/public/fad/what-is-a-derm American Academy of Family Physicians (2021). Primary Care. Available from:https://www.aafp.org
American Academy of Ophthalmology. (2022). What is an ophthalmologists? Retrieved February 28, 2022 from https://www.aao.org/eye-health/tips-prevention/what-is- ophthalmologist
American Association of Nurse Anesthesiology, 2022. Retrieved January 11, 2022, from https://www.aana.com/
American Association of Nurse Practitioners: Retrieved from, https://www.aanp.org/advocacy/state/state-practice-environment
American Association of Surgical Assistants. (2018). Job Description: Surgical Assistant. Retrieved January 12, 2022, from Microsoft Word – ASA_Job_Description_4.2.18 (surgicalassistant.org)
American Board of Dermatology. (2022). What is a Dermatologist? Retrieved January 26, 2022, from What does it mean to be Board Certified? (abderm.org)
American Board of Surgery. (2022). Training Requirements. Retrieved January 27, 2022, from https://www.absurgery.org/default.jsp?certgsqe_training
American Board of Medical Specialists, (2022). Neurology. https://www.abms.org/board/american-board-of-psychiatry-neurology/
American Board of Obstetrics and Gynecology, 2022. OB-GYN Certification. Retrieved February 28, 2022, from https://www.abog.org/specialty-certification/overview
American College of Gastroenterology (ACG), (2021). What is a Gastroenterologist? Retrieved January 27, 2022, from What is a Gastroenterologist? – American College of Gastroenterology
American College of Physicians. (2021). Nephrology: The Discipline. https://www.acponline.org/about-acp/about-internal-medicine/subspecialties-of- internal-medicine/nephrology
American College of Rheumatology. (2022). Explore rheumatology. Retrieved March 1, 2022, from https://www.rheumatology.org/I-Am-A/Student-Resident/Explore-Rheumatology
American Nursing Association (ANA). (n.d.) Retrieved from, https://www.nursingworld.org/practice-policy/workforce/what-is-nursing
American Medical Association (AMA), (2022). Nephrology (IM). Retrieved January 31, 2022, from, https://freida.ama-assn.org/specialty/nephrology-im
American Midwifery Certification Board. (2020). 2020 Demographic Report. Retrieved January 11, 2022, from https://www.amcbmidwife.org/docs/default- source/reports/demographic-report-2019.pdf?sfvrsn=23f30668_2
American Society of Hematology. (2022). Resources for Medical Students and Residents.Retrieved January 28, 2022, from Resources for Medical Students and Residents – Hematology.org
American Psychiatric Association. (2022). What is Psychiatry? Retrieved March 1, 2022, from What Is Psychiatry?
Association of Schools of Allied Health Professionals (2020). What is allied health? Retrieved from https://www.asahp.org/audiologist. (n.d.)
Miller-Keane Encyclopedia and Dictionary of Medicine, Nursing, and Allied Health, Seventh Edition. (2003). Retrieved March 3 2022 from https://medical- dictionary.thefreedictionary.com/audiologist
Bachenheimer, B. S., & ProQuest (Firm). (2019). Manual for Pharmacy Technicians: Vol. Fifth edition. ASHP.
Be an Endocrinologist: Career Information and Education Requirements. (2021). Retrieved from, https://bestaccreditedcolleges.org/articles/be-an-endocrinologist-career- information-and-education- requirements.html#:~:text=Be%20an%20Endocrinologist%3A%20Career%20Information%20and%20Education%20Requirements,%26%20Board%20Certification.%20…%205%2 0Continuing%20Education.%20
Best Accredited Colleges. (2021). Medical Recruiter: Job Description, Duties and Requirements.Retrieved March 2, 2022, from https://bestaccreditedcolleges.org/articles/medical-recruiter-job-description-duties-and-requirements.html
Build Central Incorporated. (2021). IS MEDICAL DEVICE SALES RIGHT FOR YOU? Retrieved March 2, 2022, from https://www.buildcentral.com/medical-device- sales/#:~:text=What%20does%20a%20medical%20device%20sales%20rep%20do%3F,bu yers%20and%20secures%20contracts%20to%20sell%20to%20them.
Buntat, Y., Saud, M. S., Mokhtar, M., Kamin, Y., & Feh, L. S. (2016). Important skills for biomedical services: The perspectives of Malaysian employers and employees. Work, 55(2), 481–487. https://doi.org/10.3233/WOR-162417
Bureau of Labor Statistics, U.S. Department of Labor, Occupational Outlook Handbook, Audiologists, at https://www.bls.gov/ooh/healthcare/audiologists.htm (visited January 24, 2022).
Bureau of Labor Statistics 2020 wage data and 2020-2030 employment projections “Projected growth” represents the estimated change in total employment over the projections period (2020-2030). “Projected job openings” represent openings due to growth and replacement.
Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS). Allied Health. Occupational Handbook. Retrieved from http:www.bls.gov
Bureau of Labor Statistics, U.S. Department of Labor, Occupational Outlook Handbook, Dietitians and Nutritionists,at https://www.bls.gov/ooh/healthcare/dietitians-and-nutritionists.htm (visited February 01, 2022).
Bureau of Labor Statistics, U.S. Department of Labor, Occupational Outlook Handbook, Medical Assistants,at https://www.bls.gov/ooh/healthcare/medical-assistants.htm (visited January 17,(2022).
Bureau of Labor Statistics, U.S. Department of Labor, Occupational Outlook Handbook, Medical Sonographers and Cardiovascular Technologists and Technicians,at https://www.bls.gov/ooh/healthcare/diagnostic-medical-sonographers.htm (visited January 18, 2022).
Bureau of Labor Statistics, U.S. Department of Labor, Occupational Outlook Handbook, Physical Therapists, at https://www.bls.gov/ooh/healthcare/physical-therapists.htm (visited January 07, 2022).
Bureau of Labor Statistics, U.S. Department of Labor, Occupational Outlook Handbook,Occupational Therapists, at https://www.bls.gov/ooh/healthcare/occupational-therapists.htm (visited January 18, 2022).
Bureau of Labor Statistics, U.S. Department of Labor, Occupational Outlook Handbook, Respiratory Therapists,at https://www.bls.gov/ooh/healthcare/respiratory-therapists.htm (visited January 17,2022).
Bureau of Labor Statistics, U.S. Department of Labor, Occupational Outlook Handbook, Speech-Language Pathologists,at https://www.bls.gov/ooh/healthcare/speech-language-pathologists.htm (visited January 18, 2022).
Burrows, K. E., Abelson, J., Miller, P. A., Levine, M., & Vanstone, M. (2020). Understanding health professional role integration in complex adaptive systems: a multiple-case study of physician assistants in Ontario, Canada. BMC Health Services Research, 20(1), 365. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-020-05087-8
Cambridge College of Healthcare Technology-CCHT. (2022). What Is a Patient Care Technician? Retrieved January 12, 2022, from https://www.cambridgehealth.edu/blog/what-is-a- patient-care-technician-mfbc/cardiology. (n.d.) Farlex Partner Medical Dictionary. (2012). Retrieved January 24 2022 from https://medical-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com/cardiology
Cawley, J. F. (1991). Hospital physicians’ assistants: Past, present and future. (cover story).Hospital Topics, 69(3), 14. https://doi.org/10.1080/00185868.1991.9948460
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 2022. COVID Data Tracking. https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/#cases_casesper100klast7days
Eske, J. (2020). What to know about pulmonologists. Retrieved March 1, 2022 from, What is apulmonologist? Everything you need to know (medicalnewstoday.com)
EveryNurse. (2021). Nurse Practitioner (NP). Retrieved from, https://everynurse.org/careers/nurse-practitioner/
Falcon, C. R. (2019). Pulmonary medicine. Magill’s Medical Guide (Online Edition).
Freida. AMA. (2022). Hematology (IM). Retrieved January 28, 2022, from FREIDA Hematology(IM) Residency and Fellowship Listing (ama-assn.org)Fry, J., editor. , ed. Primary Care. London: Heineman, 1980.
Furfari, A. (2017). Oncology: the Promising Future of Biomarkers. Nova Science Publishers, Inc. General Pharmaceutical Council (GPHC), 2022. What does a pharmacist do? Retrieved January 18, 2022, from https://www.pharmacyregulation.org/raising-concerns/raising-concerns-about-pharmacy-professional/what-expect-your-pharmacy/what-does-0 Generalist. (n.d.) Farlex Partner Medical Dictionary. (2012). Retrieved December 14 2021 fromhttps://medical-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com/generalist
Gleason, B. (2021). Certified Nursing Assistant (CNA) Career Overview. Retrived January 12, 2022, from https://nursejournal.org/cna/#:~:text=A%20certified%20nursing%20assistant%20%28C NA%29%20works%20under%20a,hygiene%20and%20ensure%20they%20can%20move%20about%20safely.
Global Knowledge Exchange Network (GKEN). (2009). An Overview of Education and Training Requirements for Global Healthcare Professionals. Available from http://gken.org/Docs/Workforce/Physician%20Educ%20Reqs_FINAL%20102609.pdf
Health Careers of Ohio, C. (1973). Physician Assistant Programs. Summary. Third Revised Edition.
Healey, J. (2017). Fighting Infectious Diseases. The Spinney Press.hematology. (n.d.) Medical Dictionary for the Health Professions and Nursing. (2012). Retrieved January 28 2022 from https://medical-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com/hematology
Hocking, J., Crowley, D., & Cawley, J. F. (2013). Physician Assistant Education: An Analysis of the Journal of Physician Assistant Education. Journal of Physician Assistant Education (Physician Assistant Education Association), 24(2), 6–11.
Hughes, K. (2022). Pharmaceutical Sales Representative. Salem Press Encyclopedia.
Institute for Career Research. (2010). Careers in Anesthesiology : Anesthesiologist Medical Doctor, Anesthesiologist Assistant. Institute for Career Research.
Institute of Medicine (US) Committee on the Future of Primary Care; Donaldson M, Yordy K, Vanselow N, editors. Defining Primary Care: An Interim Report. Washington (DC): National Academies Press (US); 1994. Part 3, The New Definition and an Explanation of Terms. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK231308/
Institute of Medicine (US) Committee on the Future of Primary Care; Donaldson MS, Yordy KD, Lohr KN, et al., editors. Primary Care: America’s Health in a New Era. Washington (DC): National Academies Press (US); 1996. 2, Defining Primary Care. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK232631
IOM. Community-Oriented Primary Care: A Practical Assessment . Volume I. The Committee Report. Washington, D.C.: National Academy Press, 1984. [PubMed: 25032438]
Joyner, J. (2018). Roles and responsibilities of a Cardiologist. Retrieved January 24, 2022, from Roles & Responsibilities of a Cardiologist (chron.com)
Kozikowski, A., Mauldin, S., Jeffery, C., Kavanaugh, K., Barnhill, G., & Morton-Rias, D. (2021). Public Knowledge and Beliefs Regarding Licensure, Certification and Medical Education of Physician Assistants. Journal of Medical Regulation, 107(1), 26–34. https://doi.org/10.30770/2572-1852-107.1.26
Kulo, V., Fleming, S., Gordes, K. L., Jun, H.-J., Cawley, J. F., & Kayingo, G. (2021). A physician assistant entry-level doctoral degree: more harm than good? BMC Medical Education, 21(1), 274. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-021-02725-5
Lopez, E.O., Ballard, B.D., & Jan, A. (2021). Cardiovascular Disease. In: StatPearls [Internet].
Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2022 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK535419/
Matsen J. M. (1987). The role of infectious disease physicians in hospital clinical microbiology laboratories. Bulletin of the New York Academy of Medicine, 63(6), 605–611.
Medical doctor. (n.d.) Miller-Keane Encyclopedia and Dictionary of Medicine, Nursing, and Allied Health, Seventh Edition. (2003). Retrieved December 14 2021 from https://medical-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com/Medical+doctor
Merkle, F., Ritsema, T. S., Bauer, S., & Kuilman, L. (2011). The physician assistant: Shifting the Paradigm of European medical practice? HSR Proceedings in Intensive Care & Cardiovascular Anesthesia, 3(4), 255–262.
Metropolitan Washington Regional Medical Program, W. D. (1970). The Physician’s Assistant; An Approach to Improved Patient Care.
Mir, M. A. (2020). Basics and Fundamentals of Immunology. Nova Medicine and Health. Moragne, W. (1999). ASTHMA. Allergies (0-7613-1359-1), 90.
Morgan, P. A., Strand, J., Østbye, T., & Albanese, M. A. (2007). Missing in Action: Care by Physician Assistants and Nurse Practitioners in National Health Surveys. Health Services Research, 42(5), 2022–2037. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1475-6773.2007.00700.x
National Board of Certification & Recertification for Nurse Anesthetists-NBCRNA. (2022). Initial Certification. Retrieved January 11, 2022, from Initial Certification | NBCRNA
National Center for O*NET Development. Medical and Clinical Laboratory Technologists- 29-2011.00. O*NET Code Connector. Retrieved February 9, 2022, from https://www.onetcodeconnector.org/ccreport/29-2011.00
National Center for O*NET Development. Occupational Therapists – 29- 1122.00. O*NET Code Connector. Retrieved February 9, 2022, from https://www.onetcodeconnector.org/ccreport/29-1122.00
National Center for O*NET Development. Physical Therapist Assistants – 31- 2021.00. O*NET Code Connector. Retrieved February 9, 2022, from https://www.onetcodeconnector.org/ccreport/31-2021.00
National Center for O*NET Development. Speech-Language Pathologists – 29- 1127.00. O*NET Code Connector. Retrieved February 9, 2022,
from https://www.onetcodeconnector.org/ccreport/29-1127.00
National Center of Education Statistics (2021). Dietician program. Retrieved fromhttps://nces.ed.gov/ipeds/cipcode/cipdetail.aspx?y=55&cipid=88788
National Center of Education Statistics (2021). Medical Sonographer Program.
Retrieved from https://nces.ed.gov/ipeds/cipcode/cipdetail.aspx?y=55&cipid=88788
National Center of Education Statistics (2021). Respiratory Therapist Program.Retrieved from https://nces.ed.gov/ipeds/cipcode/cipdetail.aspx?y=88786
National Center of Education Statistics (2021). Diagnostic Medical Sonography/sonographer and ultrasound technician program. Retrieved from https://nces.ed.gov/ipeds/cipcode/cipdetail.aspx?y=55&cipid=88748
National Center of Education Statistics (2021) Speech Language Pathology Program.Retrieved from https://nces.ed.gov/ipeds/cipcode/cipdetail.aspx?y=55&cipid=88748
National Council of State Boards of Nursing (2020). NCSBN’s environmental scan: A portrait of nursing and healthcare in 2020 and beyond. Journal of Nursing Regulation. 10(4), S1- S36.
National Kidney Foundation. (2015). Kidney Basics. Retrieved January 31, 2022, from, https://www.kidney.org/professionals
Neurology. (n.d.) Farlex Partner Medical Dictionary. (2012). Retrieved February 28 2022 from https://medical-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com/neurology
Niles, N.J. (2020). Basic concepts of healthcare human resource management. 2nd edition. Jones and Bartlett: Burlington, MA.
Niles, N. J. (2018). Basic of the U.S. health care system. 3rd edition. Jones and Bartlett: Burlington, MA.
Number of active physicians in the U.S. in 2021, by specialty area. Retrieved January 26, 2022, from https://www.statista.com/statistics/209424/us-number-of-active-physicians-by-specialty-area/
ONET Online (2022). Occupation: Neurologist. Retrieved from https://www.onetonline.org/link/summary/29-1217.00
ONET Online (2022). Occupation: Physical Therapist. Retrieved from 29-1123.00 – Physical Therapists (onetonline.org)
ONET Online (2022). Occupation: Respiratory Therapist. Retrieved from 29-1126.00 – Respiratory Therapists (onetonline.org)
ophthalmology. (n.d.) Collins Dictionary of Medicine. (2004, 2005). Retrieved February 28 2022 from https://medical-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com/ophthalmology
OTA (Office of Technology Assessment). Nurse Practitioners, Physician Assistants, and Certified Nurse-Midwives: A Policy Analysis. Health Technology Case Study 37. Publ. No. OTA- HCS-37. Washington, D.C.: U.S. Government Printing Office, 1986.
Oweida, A. B. S. . M. S. (2020). Radiology and Medical Imaging. Salem Press Encyclopedia of Science.
Patient Navigator Training Collaborative. (2011). Introduction to the Healthcare System. A tutorial for Patient Navigators. Module 1: Healthcare systems. Retrieved January 18, 2022. From http://www.patientnavigatortraining.org/healthcare_system/module1/2_typesofpatien tcare.htm
Petersen, E., Chen, L.H., & Schlagenhauf-Lawlor, P. (2011). Infectious Diseases : A Geographic Guide. Wiley.
Pew Health Professions Commission. Nurse Practitioners: Doubling the Graduates by the Year 2000. San Francisco: Pew Health Professions Commission, 1994.
Physician assistant. (1983). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.
Piotrowski, N. A., PhD. (2019). Psychiatry. Magill’s Medical Guide (Online Edition).
Polansky M. (2007). A historical perspective on postgraduate physician assistant education and the association of postgraduate physician assistant programs. Journal of Physician Assistant Education (Physician Assistant Education Association), 18(3), 100–108. https://doi.org/10.1097/01367895-200718030-00014
Powers, J., & Whitehead, PO. (2022). 2022 CNS Trends Look Good In the New Year. Retrieved January 6, 2022, from https://nacns.org/2022/01/2022-cns-trends-look-good-in-the- new-year/
RegisteredNursing.org. (2021). Clinical Nurse Specialist Certification. Retrieved January 6, 2022, from https://www.registerednursing.org/certification/clinical-nurse- specialist/#:~:text=To%20become%20certified%20as%20an%20adult- gerontology%20CNS%2C%20applicants,advanced%20pharmacology%2C%20and%20an%20advanced%20health%20assessment%20course
rheumatology. (n.d.) Gale Encyclopedia of Medicine. (2008). Retrieved March 1 2022 from https://medical-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com/rheumatology
Ross, N., Parle, J., Begg, P., & Kuhns, D. (2012). The case for the physician assistant. Clinical Medicine, 12(3), 200–206. https://doi.org/10.7861/clinmedicine.12-3-200
Samantha Simon. (2017). Nurses. National Highlights Inc.
Santiago, A. (2020). Differences Between Clinical and Non-Clinical Medical Jobs. Retrieved January 11, 2022, from Clinical vs. Non-Clinical Medical Jobs (verywellhealth.com)
Santiago, A.C. (2020). What Is a Medical Technologist? Retrieved March 2, 2022, from https://www.verywellhealth.com/medical-technologist-career-profile-1736165
Schnur, M.B. (2020). U.S. Nurses in 2020: Who We Are and Where We Work. Retrieved January 5, 2022 from, https://www.nursingcenter.com/ncblog/may-2020/u-s-nurses-in-2020
Shi, L., and Singh, D. A. (2019). Delivering health care in America: A systems approach 7th Edition. Jones and Bartlett: Burlington, MA.
Shuman, R. B., PhD. (2019). Oncology. Salem Press Encyclopedia of Health.
Shuman, R. B., PhD. (2019). Otorhinolaryngology. Magill’s Medical Guide (Online Edition). Shniper, L. (2001). Medical transcriptionists: Making medical histories. Occupational OutlookQuarterly, 45(3), 34.
Society for Endocrinology. What is Endocrinology? Retrieved January 26, 2022, from https://www.endocrinology.org/about-us/what-is-endocrinology/
Spenkelink-Schut G, ten Cate OTJ, & Kort HSM. (2008). Training the physician assistant in the Netherlands. Journal of Physician Assistant Education (Physician Assistant Education Association), 19(4), 46–53. https://doi.org/10.1097/01367895-200819040-00037
Stefl, M.E. (2008). Common Competencies for All Healthcare Managers: The Healthcare Leadership Alliance Model. Journal of Healthcare Management 53(6), p.360-373.Retrieved from common competencies for all healthcare managers.pdf(healthcareleadershipalliance.org)
The American Board of Allergy and Immunology. Requirements for Certification. Retrieved January 19, 2022, from https://www.abai.org/CerRequire.asp
The American Board of surgery, (2021). Retrieved January 27, 2022, from http://www.absurgery.org/
The National Association of Clinical Nurse Specialists (NACNS), (2016). CNS Scope of Practice and Prescriptive Authority. Retrieved January 6, 2022, from http://nacns.org/wp- content/uploads/2016/11/PractPrescAuthority1605.pdf
The RN Licensing Process. Retrieved from, https://www.nursinglicensure.org/articles/rn- licensing/
Timmerman, G.L. (2022). General Surgery. American College of Surgeons. Retrieved from, https://www.facs.org/education/resources/residency- search/specialties/general#:~:text=%22General%20Surgery%22%20is%20a%20discipline%20of%20surgery%20having,neoplasia%2C%20which%20are%20common%20to%20all%20surgical%20specialties.
Turner, B. J., & Laine, C. (2001). Differences between generalists and specialists: knowledge, realism, or primum non nocere?. Journal of general internal medicine, 16(6), 422–424. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1525-1497.2001.016006422.x
UCLA (2018). Obstetricians and gynecologists: What’s the difference? Retrieved February 28, 2022, from https://medschool.ucla.edu/body.cfm?id=1158&action=detail&ref=1051
Ultimate Medical Academy-UMA. (2021). What Is a Patient Care Technician? Career Overview and Outlook. Retrieved January 12, 2022, from https://www.ultimatemedical.edu/blog/what-is-a-patient-care-technician-career-overview-and-outlook/
U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics 2020 Occupational Employment Statistics, Biology Technicians; Medical Assistants; Phlebotomist; Clinical Laboratory Technologists and Technicians. O*Net, Cytotechnologists
U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. (2021). Dental hygienists. Retrieved January 25, 2022, from https://www.bls.gov/ooh/Healthcare/Dental-hygienists.htm
U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. (2021). Occupational Employment and Wage statistics: Nurse Midwives. Retrieved January 11, 2022, from Nurse Midwives (bls.gov)
US. Bureau of Labor Statistics, 2021. Medical Equipment Repairer. Retrieved March 2, 2022, from Medical Equipment Repairers: Occupational Outlook Handbook: : U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (bls.gov)
US. Bureau of Labor Statistics, 2021. Secretaries and Administrative assistants. Retrieved March 2, 2022, from Secretaries and Administrative Assistants: Occupational Outlook Handbook: : U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (bls.gov)
US. Bureau of Labor Statistics, 2021. Wholesale representatives. Retrieved March 2, 2022, from Wholesale and Manufacturing Sales Representatives : Occupational Outlook Handbook: U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (bls.gov)
US. Bureau of Labor Statistics, 2021. Bioengineer or Biomedical Engineer. Retrieved March 2, 2022, https://www.bls.gov/ooh/architecture-and-engineering/biomedical- engineers.htm#tab-4
Vezina, K. M. (2018). Biomedical Engineering. Salem Press Encyclopedia of Science.
Wallace, E. K., PhD, & Fallon, L. F. J., MD. (2019). Orthopedics. Magill’s Medical Guide (Online Edition).
Wiesen, K. (2021). The Role and Scope of Practice of the Nurse Practitioner. Retrieved from, The Role and Scope of Practice of the Nurse Practitioner | EveryNurse.org
Williams, E. (n.d.). Job Description for an Infectious Disease Physician. Retrieved January 31, 2022, from https://work.chron.com/job-description-infectious-disease-physician- 17104.html
Wolper, L. F. (2013). Physician practice management: Essential operational and financial knowledge. Jones and Bartlett: Burlington, MA.
Young, A., Chaudhry, H.J., Pei, X., Arnhart, K., Dugan, M., Simons, K.B. (2021). FSMB Census of Licensed Physicians in the United States, 2020. JOURNAL of MEDICAL REGULATION,107(2). 57-64. Available at https://www.fsmb.org/siteassets/advocacy/publications/2020-physician-census.pdf
Zhang, X., Lin, D., Pforsich, H., & Lin, V. W. (2020). Physician workforce in the United States of America: forecasting nationwide shortages. Human resources for health, 18(1), 8. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12960-020-0448-3
Zippia, 2022. CERTIFIED NURSING ASSISTANT Demographics and Statistics in the US. Retrieved January 12, 2022, from https://www.zippia.com/certified-nursing-assistant-jobs/demographics/